Team:Freiburg Transfection and Synthetic Receptor
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
'''Figure 2_Transfection: Structure of the signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP construct. Extracellular: Lipocalin, GGGSlinker; Transmembrane: transmembraneregion of the EGF-receptor; Intracellular: Split-beta-Lactamase1, YFP.'''<br> | '''Figure 2_Transfection: Structure of the signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP construct. Extracellular: Lipocalin, GGGSlinker; Transmembrane: transmembraneregion of the EGF-receptor; Intracellular: Split-beta-Lactamase1, YFP.'''<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
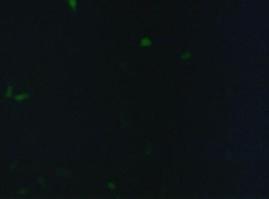
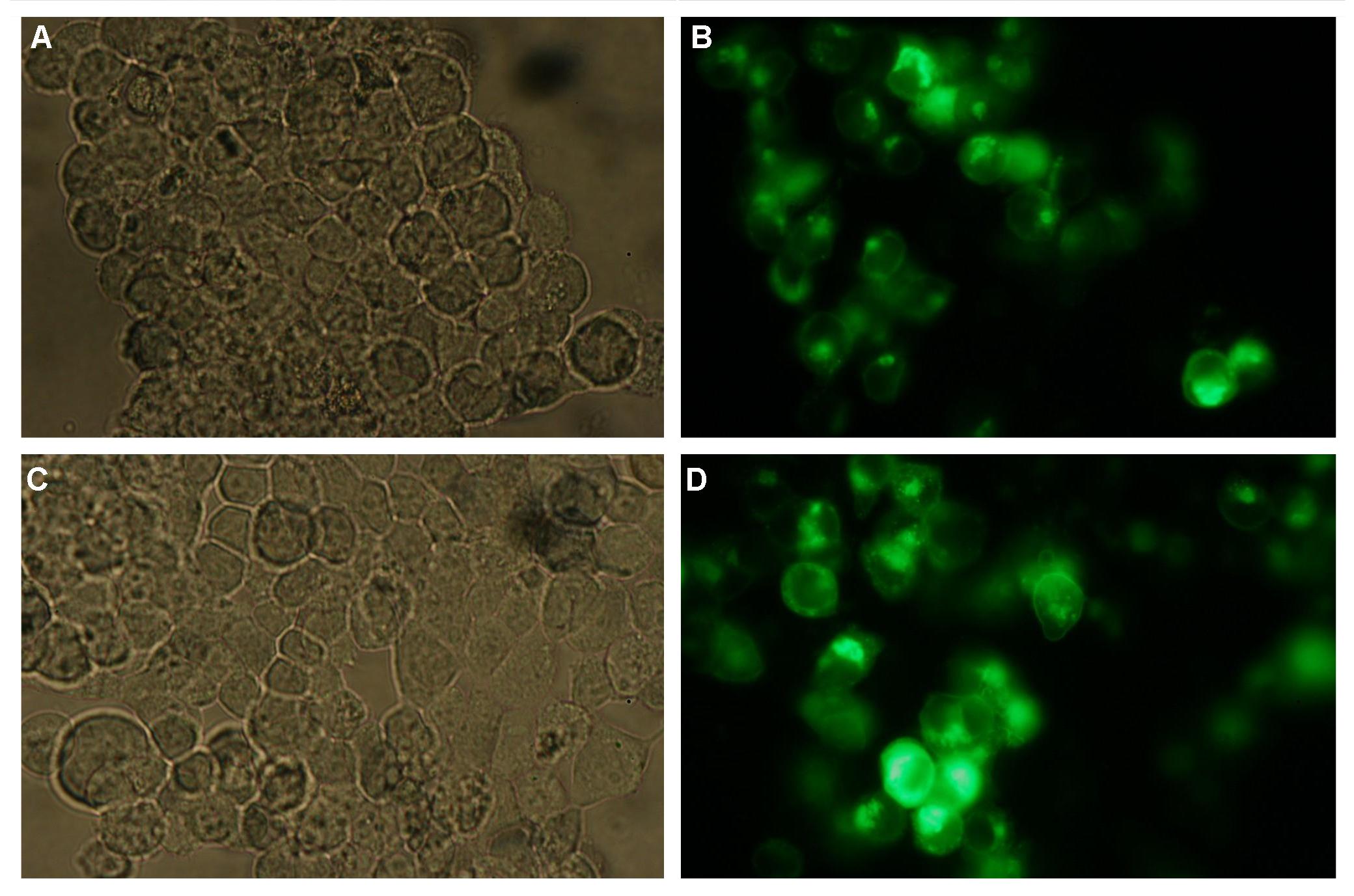
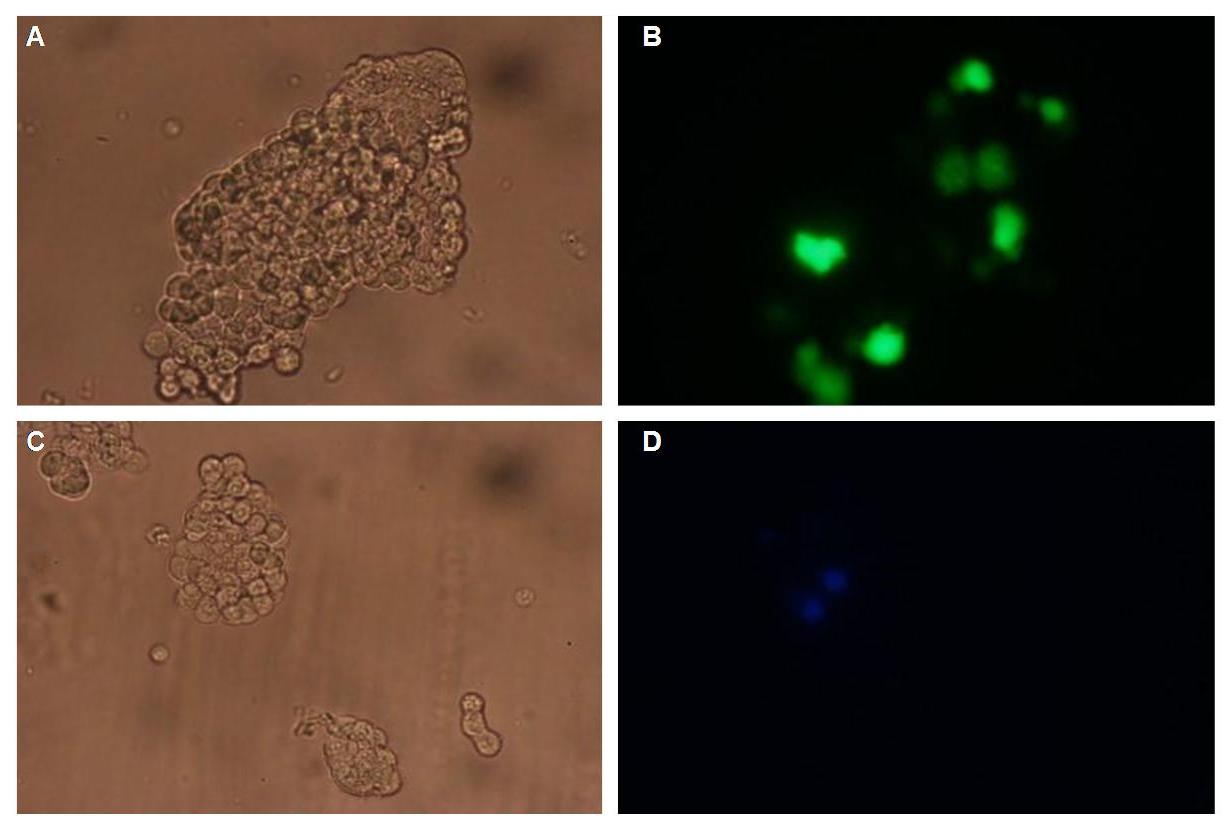
| - | Membranelocalization of the construct signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP is visible in transfected 293T cells (Figure 3_Transfection). The fluorescence of the cells is most likely restricted to the cellmembrane | + | Membranelocalization of the construct signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP is visible in transfected 293T cells (Figure 3_Transfection). The fluorescence of the cells is most likely restricted to the cellmembrane as evident by the strong signal at the surface of the cell spheres confirming the assembly of the construct in the cytoplasmamembrane.<br> |
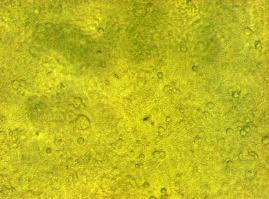
In comparison, 293T cells transfected with the construct transfectionvector-CMV-YFP show a uniformly distributed fluorescence all-over the cell (Figure 4_Transfection A and B).<br> | In comparison, 293T cells transfected with the construct transfectionvector-CMV-YFP show a uniformly distributed fluorescence all-over the cell (Figure 4_Transfection A and B).<br> | ||
| - | Transfection with the construct transfectionvector-CMV-CFP as well results in completely fluorescent cells (Figure 4_Transfection C and D).<br> | + | Transfection with the construct transfectionvector-CMV-CFP, i.e. membrane targeting as well results in completely fluorescent cells (Figure 4_Transfection C and D).<br> |
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:Freiburg2008_SP_LIPO_GGGS_TM_bla1_YFP_1.jpg|710px]]<br> | [[Image:Freiburg2008_SP_LIPO_GGGS_TM_bla1_YFP_1.jpg|710px]]<br> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<h4>'''Double transfections with Splitfluorophor-/Splitenzyme-constructs'''</h4> | <h4>'''Double transfections with Splitfluorophor-/Splitenzyme-constructs'''</h4> | ||
| - | + | Figure 5_Transfection gives the model of the Anticalin fused to the GGGSlinker, the transmembrane domain and the N-terminal part of Cerulean CFP or the C-terminal part of Cerulean CFP. The signalpeptide is not displaeyd. the structures of the signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-nCFP and signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-fluolinker-cCFP constructs are visible (exemplary for the Splitfluorophore-/Splitenzyme-constructs). The extracellular fragment is build of fluorescein binding Anticalin and a GGGSLinker. Intracellular either the N-terminal part or the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophore is fused to the transmembrane region of the EGF-receptor. To achieve more flexibility and to support the assembly of the two splitfluorophore parts a fluolinker is fused in between the transmembrane region and the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophores.<br> | |
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:Freiburg2008_Lipo+Split_CFP.jpg|450px]]<br> | [[Image:Freiburg2008_Lipo+Split_CFP.jpg|450px]]<br> | ||
Revision as of 15:42, 29 October 2008
 "
"