Team:Harvard/Parts
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Results) |
(→lac system (will be moved to separate page)) |
||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
Many genes are involved in Shewanella’s complex respiratory system (Heidelberg et al. 2002). We focused on mtrB, a 679-amino-acid-long outer membrane protein thought to be involved in the binding of metals and the localization of outer membrane cytochromes during reduction (Bretschger et al. 2007). It is unfortunately toxic in E. coli (Saffarini). Bretschger et al. recently characterized the role of mtrB in anaerobic respiration of Shewanella by looking at the effects of knock-out and complementation of mtrB on the electrical output of Shewanella. It was found that the strain which lacked mtrB produced less than 20% of the current generated by the wild type strain. In complemented strains, where mtrB is expressed constitutively under the control of the lacZ promoter in the knock-out strain, the phenotype was rescued with a similar amount of current being produced to that of the wild type (Bretschger et al. 2007). Not only does this experiment demonstrate the importance of mtrB in reduction in Shewanella, it also suggests a mechanism by which this electrical output could be controlled. Transforming plasmids containing mtrB under the control of an inducible promoter into mtrB knock out Shewanella, would conceivably create a strain of Shewanella which could increase its electrical output in response to the turning-on of the promoter controlling mtrB expression. The creation of a strain with an inducible electrical output could have important applications in biotechnology by creating a system which couples the ability of Shewanella to respond to a diverse array of stimuli with the speed and ubiquity of electricity. | Many genes are involved in Shewanella’s complex respiratory system (Heidelberg et al. 2002). We focused on mtrB, a 679-amino-acid-long outer membrane protein thought to be involved in the binding of metals and the localization of outer membrane cytochromes during reduction (Bretschger et al. 2007). It is unfortunately toxic in E. coli (Saffarini). Bretschger et al. recently characterized the role of mtrB in anaerobic respiration of Shewanella by looking at the effects of knock-out and complementation of mtrB on the electrical output of Shewanella. It was found that the strain which lacked mtrB produced less than 20% of the current generated by the wild type strain. In complemented strains, where mtrB is expressed constitutively under the control of the lacZ promoter in the knock-out strain, the phenotype was rescued with a similar amount of current being produced to that of the wild type (Bretschger et al. 2007). Not only does this experiment demonstrate the importance of mtrB in reduction in Shewanella, it also suggests a mechanism by which this electrical output could be controlled. Transforming plasmids containing mtrB under the control of an inducible promoter into mtrB knock out Shewanella, would conceivably create a strain of Shewanella which could increase its electrical output in response to the turning-on of the promoter controlling mtrB expression. The creation of a strain with an inducible electrical output could have important applications in biotechnology by creating a system which couples the ability of Shewanella to respond to a diverse array of stimuli with the speed and ubiquity of electricity. | ||
| - | === | + | ===Lac system (will be moved to separate page)=== |
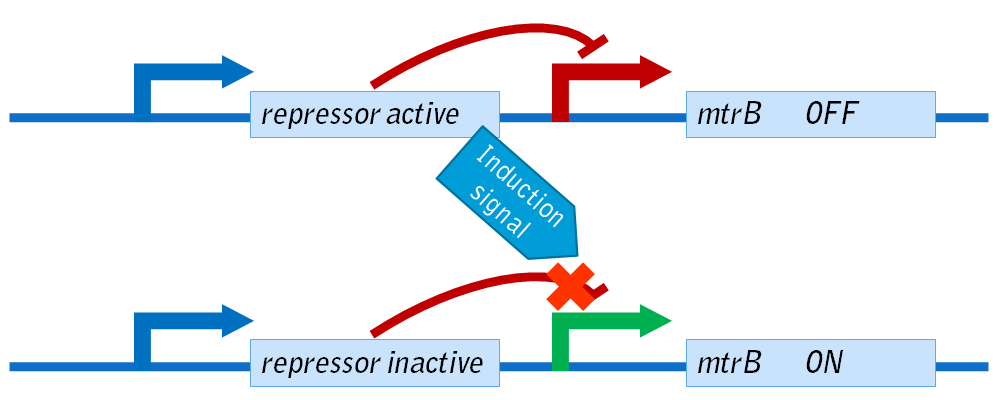
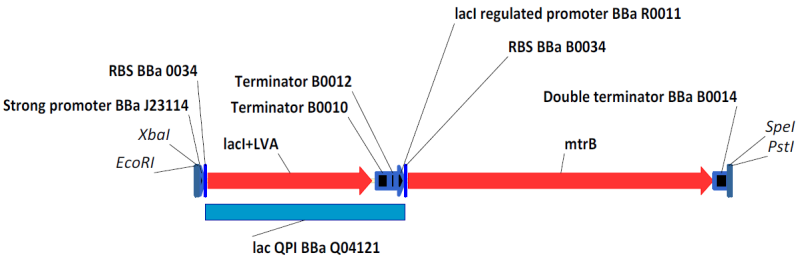
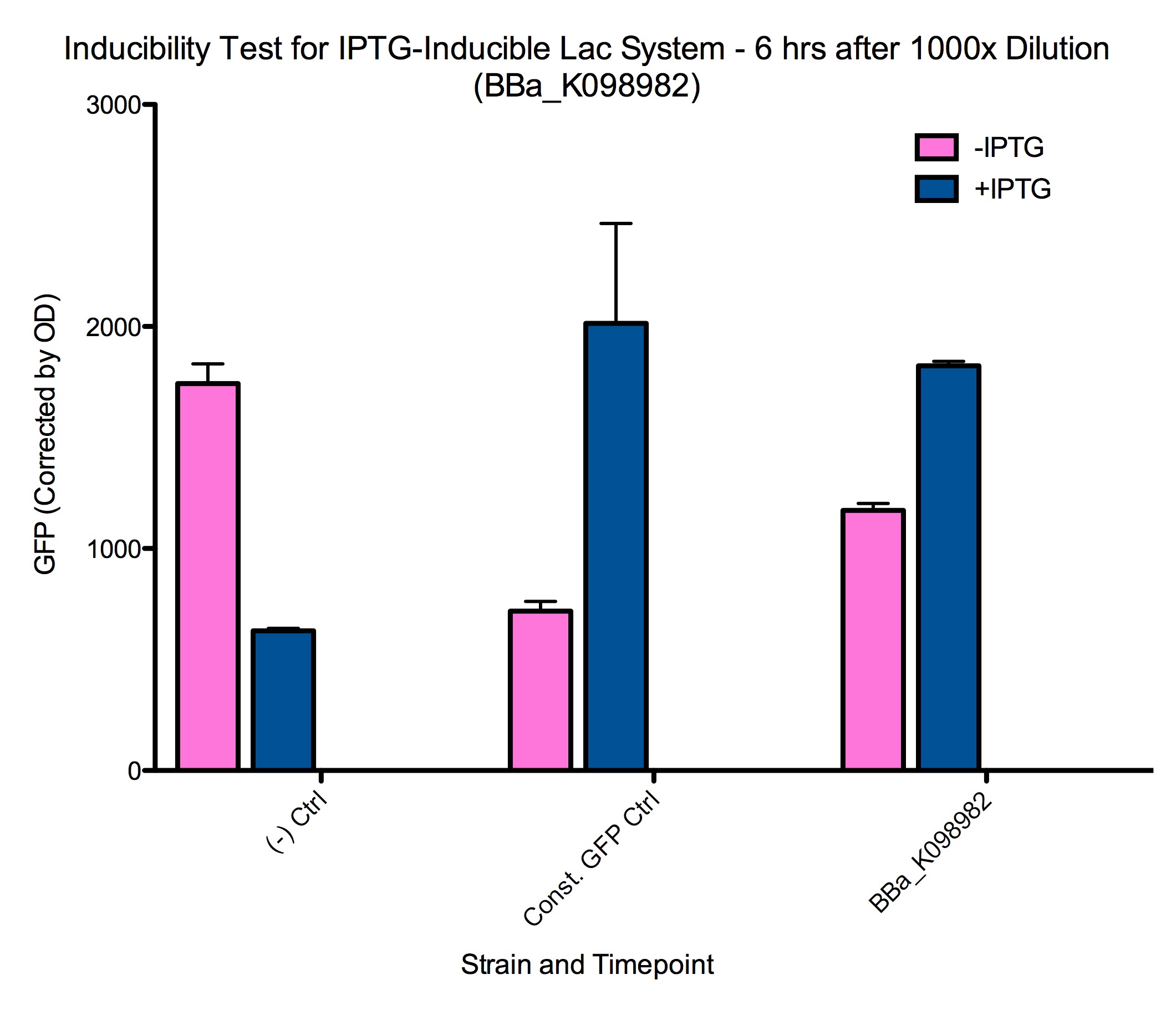
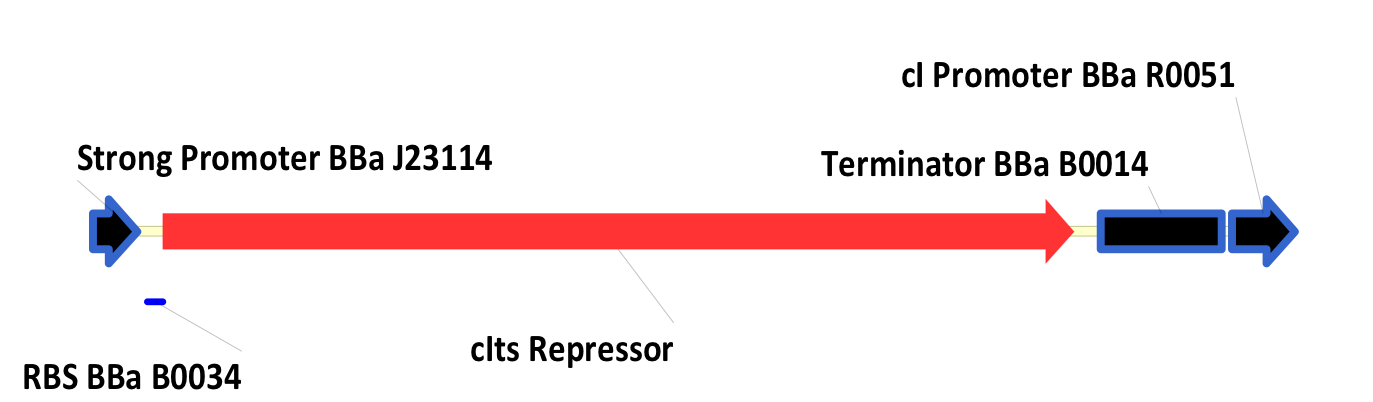
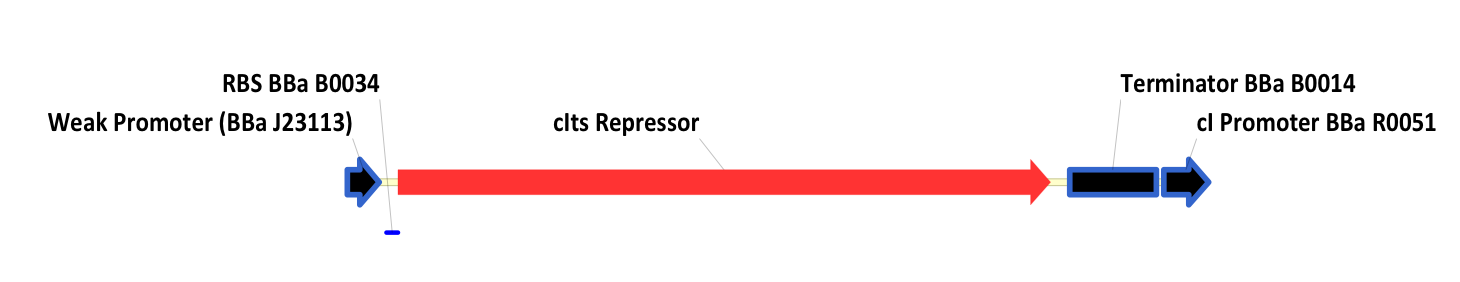
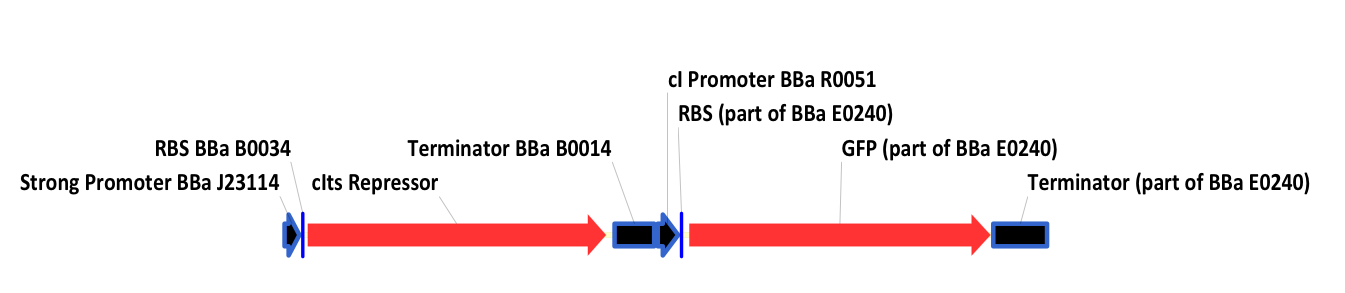
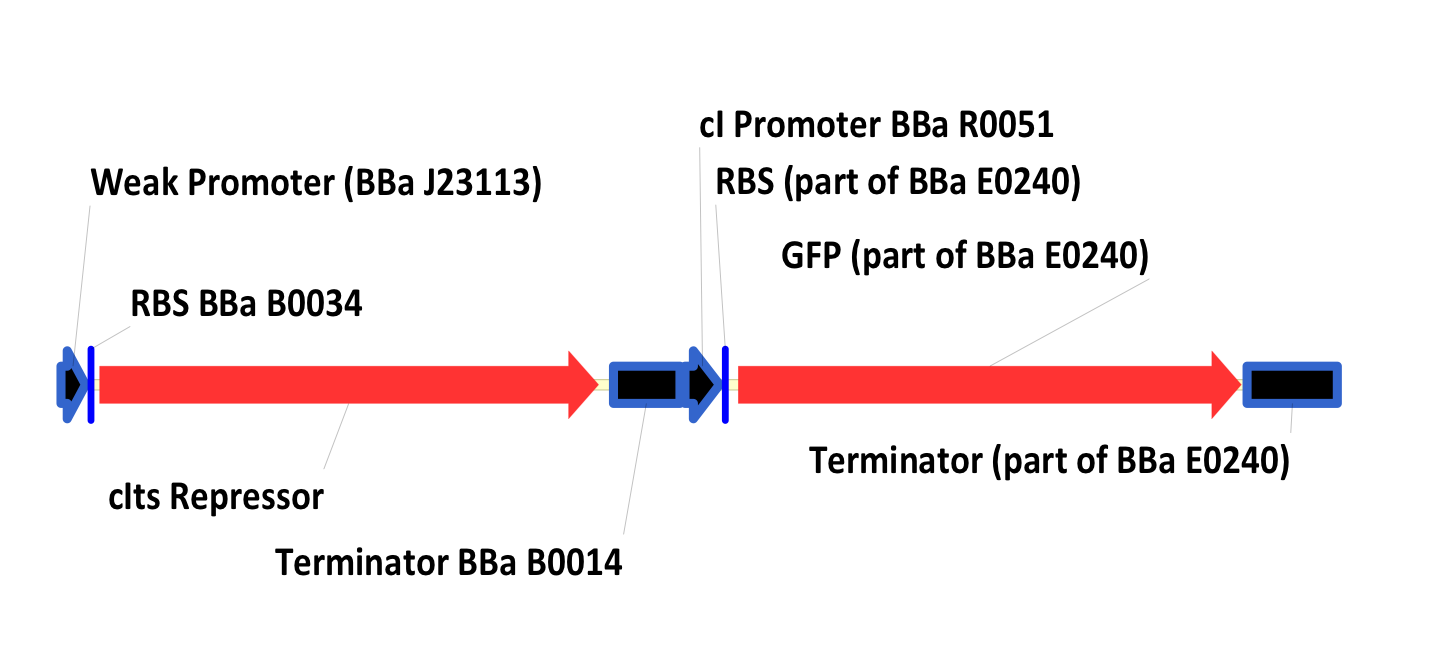
| - | + | In this system, the lac repressor (LacI) is controlled by a strong constitutive promoter, and is upstream of mtrB under the control of pLac, a LacI regulated promoter. In the default state, LacI is expressed, and inhibits transcription at pLac. Thus, in the default state, mtrB is not expressed. IPTG (an analog of allolactose) induces mtrB expression by binding to LacI, thereby preventing it from inhibiting transcription at pLac. | |
| + | |||
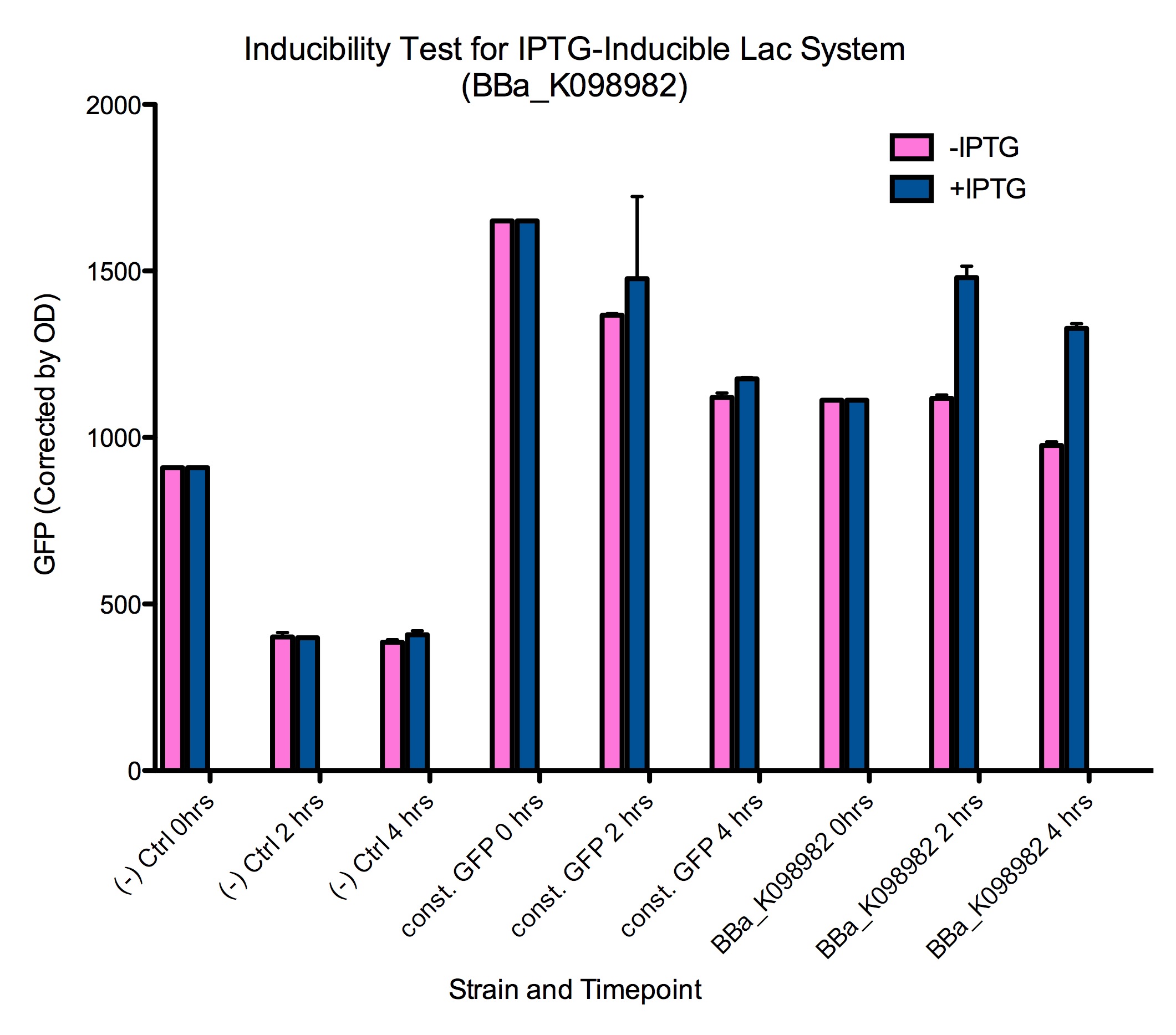
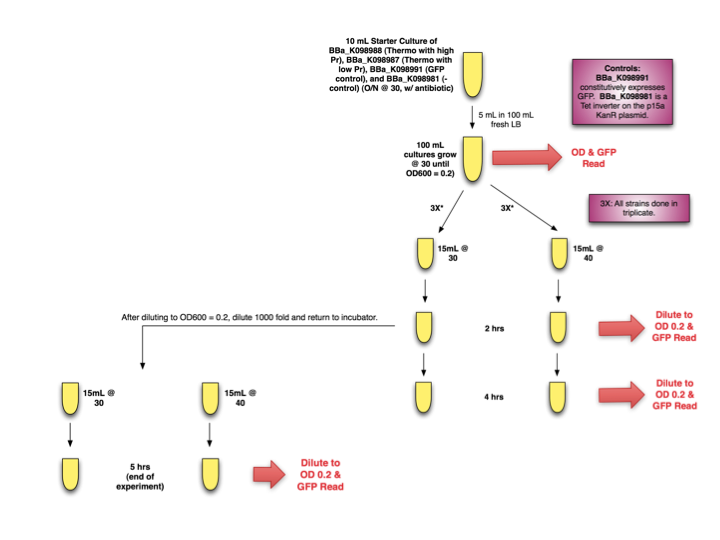
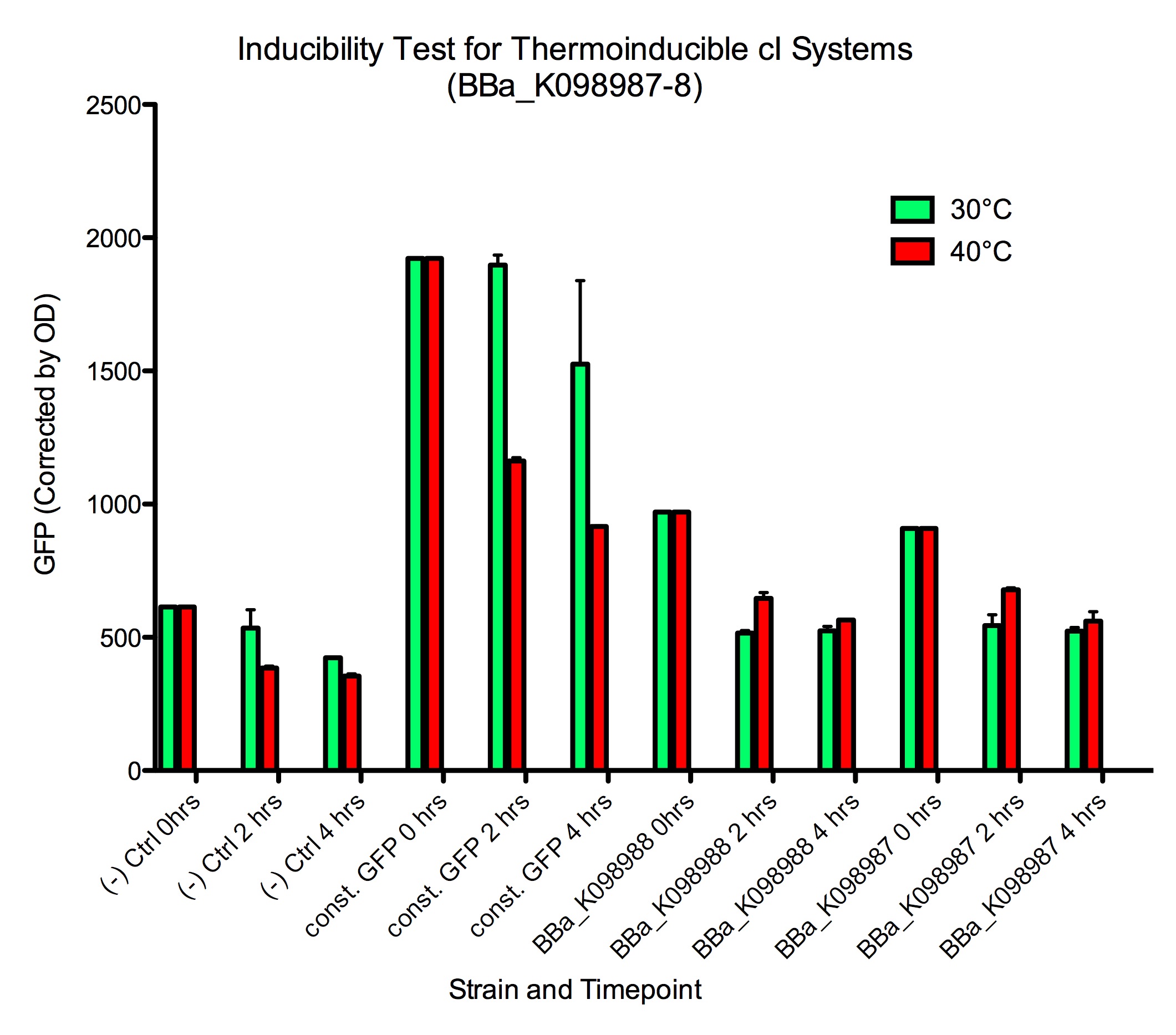
Amy's induction data | Amy's induction data | ||
use sublevels, as entire section will become new page | use sublevels, as entire section will become new page | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 29 October 2008
 "
"