|
_Transfection
1) Localization at the cell membrane
To show the localization of the constructs at the cell membrane transfection of the construct signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP was performed.
Figure 1_Transfection shows the configuration of the construct. Lipocalin, the fluorescein binding Anticalin, exhibits the extracellular part of the construct. The transmembrane region is appropriate to that of the EGF-receptor erbb1. Split-beta-Lactamase, the intracellular part is labeled to the yellow fluorescent protein to detect membrane localization.

Figure 1_Transfection
Membranelocalization of the construct signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-betaLactamase1-YFP is visible in transfected 293T cells (Figure 2_Transfection). The fluorescence of the cells is most likely restricted to the cellmembrane which confirms the assembly of the construct in the cytoplasmamembrane.
In comparison, 293T cells transfected with the construct transfectionvector-YFP show a uniformly distributed fluorescence all-over the cell (Figure 3_Tansfection A and B).
Transfection with the construct transfectionvector-CFP as well results in completely fluorescent cells (Figure 3_Transfection C and D).
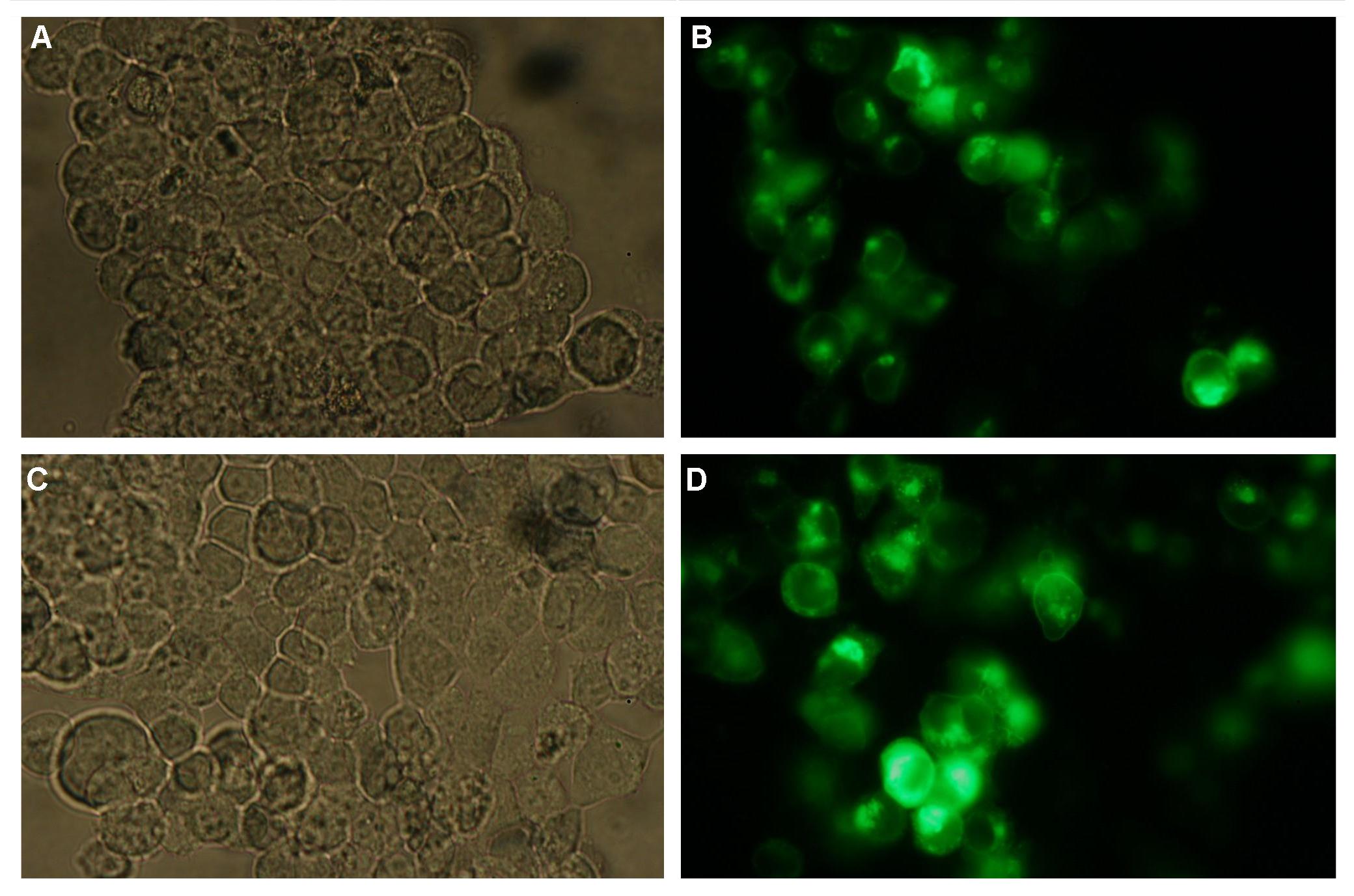
Figure 2_Transfection
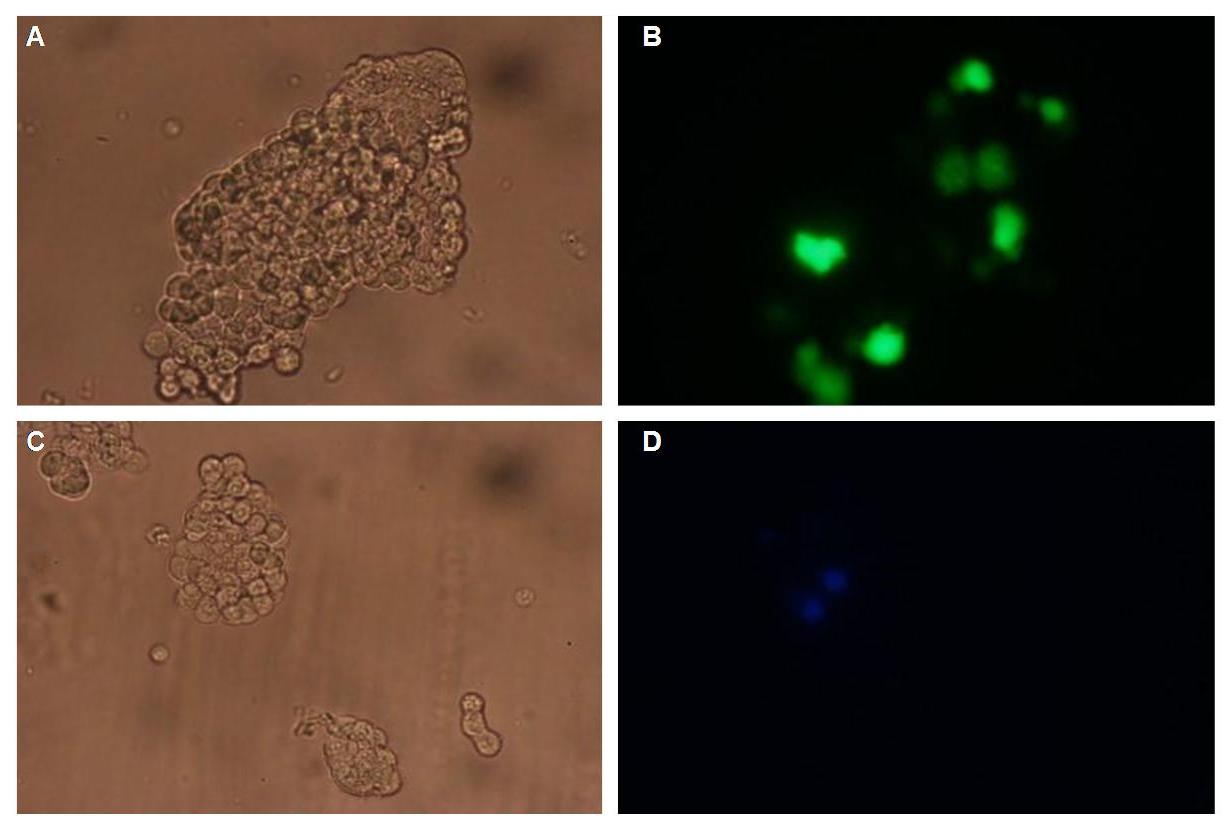
Figure 3_Transfection
2) Double transfections with Splitfluorophor-/Splitenzyme-constructs
On Figure 4_Transfection the structures of the signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-nCFP and signalpeptide-Lipocalin-transmembraneregion-fluolinker-cCFP are visible (exemplary for the Splitfluorophore-/Splitenzyme-constructs). The extracellular fragment is build of Lipocalin (fluorescein binding Anticalin) and a GGGSLinker. Intracellular either the N-terminal part or the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophore is fused to the transmembrane region of the EGF-receptor. To achieve more flexibility and to support the assembly of the two splitfluorophore parts a fluolinker is fused in between the transmembrane region and the C-terminal part of the splitfluorophores.

Figure 4_Transfection
Adding fluorescein-coupled molecules leads to a clustering of the Lipocalin constructs due to the fluorescein-Lipocalin-binding. Similarly Nip-coupled molecules and Nip constructs.
The clustering of the constructs in turn results in an assembly of the splitfluorophores or splitenzymes and therefore creates a functional protein (Figure 5_Transfection).

Figure 5_Transfection
METHODS
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Transfection of 293T cells
One day before transfection cells were counted in the Neubauer chamber and 6*10^4 cells/cm² were seeded in 6 well plates. Approximately 1 hour before transfection cells were washed with 1xPBS and fresh DMEM medium was added. For transfection 2µg of DNA were mixed with 25µl CaCl2 and ddH2O was filled up to 250µl. After an incubation on ice for 20 min 250µl BBS (2x) were added. This mixture was given to the cells and after 4-12 hours cells were washed and fresh medium was added.
|