|
Model Construction
Description
- We chose to use a chemostat. We want to impose to our model the fact that the rate of production has to be proportional to the existing population and to the amount of available resources.
- We assume a logistic model for the population kinetics in the chemostat (reference).
- To archieve synchronization we use QS. Explain the principle?
Kinetics
- Following a logistic model of the population in the chamostat, the concentration of cells in the medium can be expressed in terms of a production term and a degradation term, as:
On the one hand, the concentration of cells (c) increase exponentialy with a velocity given by the growth rate (αcell). After a certain time, the population reaches a maximum concentration (cmax).
On the other hand, c is reduced due to the dilution (Drenewal) and the cell death (d).
- Then, we need to add the death term, and a dilution term cause by the renewal of the chemostat. Finally we get :
where cmax is the carrying capacity for cell growth, and
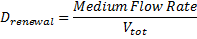 the dilution rate, d the death rate constant the dilution rate, d the death rate constant
eqHSL 1
eqHSL 2
- Activation of envZ depends of the concentration of HSL:
eqHSL 3
Parameters Search
manly from literature but also from S0 analysis.
| Parameters
|
|
|
| Chemostat
| Parameter
| Meaning
| Original Value
| Normalized Value
| Unit
| Source
|
| figure / equations of Chemostat
| αcell
| Growth rate
| 0.0198
| 1
| min-1
| wet-lab
|
| cmax
| Carrying capacity for cell growth
| 0.1
| 0.1
| µm3
| [3]
|
| Drenewal
| Dilution rate
| 0.00198
| 0.1
| min-1
| wet-lab ([3])
|
| d
| Death rate
| 0.0099
| 0.5
| min-1
| wet-lab
|
|
|
| Quorum Sensing
| Parameter
| Meaning
| Original Value
| Normalized Value
| Unit
| Source
|
| figure / equations of Quorum Sensing
| γHSL
| Degradation rate
| 0.0053
| 0.2690
| min-1
| wet-lab
|
γHSLext
| Degradation rate
| 0.0106
| 0.5380
| min-1
| [6]
|
| βHSL
| Production rate
| 0.3168
| 16
| min-1
| ∅
|
| η
| Diffusion rate
| 10
| 505
| min-1
| [2]
|
| nHSL
| Hill coefficient
|
| 4
|
| [3]
|
| θHSL
| Hill characteristic concentration for the second operator
|
| 0.5
| c.u
| [3]
|
|