Team:BrownTwo/Implementation/testing
From 2008.igem.org
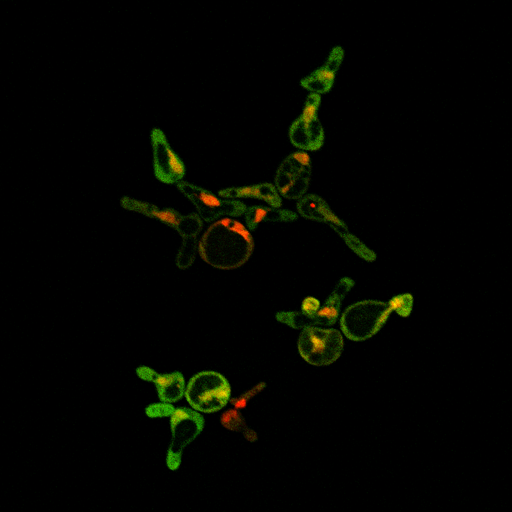
Circuit TestingWe have determined that it is necessary to characterize our parts in order to guide the construction of our device. Precisely because our system is so complex, we need to ensure that we understand the correct parts in our smaller circuits before moving on to the system as a whole. In such a case, we have outlined a few critical tests to demonstrate the proper functioning of our parts. We ran a test of our LexA activator and inducible reporter on the confocal fluorescence microscope, and saw mCherry in the nucleus and YFP in the cytoplasm as expected:
The mCherry is tagged onto the LexA activating transcription factor, and so is localized to the nucleus due to the SV40 NLS ligated just before the terminator. The YFP is generated by mCYC+LexA binding sites on a construct containing Kozak+YFP+ADH1 terminator. InputsOur proof-of-principle design incorporates the use of inducible promoters that respond to varied levels of chemical input. pMET25 is a repressible promoter that responds to levels of methionine from 0-500 uM.
Outputs
Viability TestsIn addition to testing the promoters and parts provided to us, we wish to apply our network to tests that involve Apoptosis test- induce apoptosis externally and then save cells with the limiter device! -this test has important medical relevance, seeing as many tumor phenotypes are characterized by a noted decline or absence of apoptotic activity -for yeast, extrinsically-signaled apoptosis depends on oxidative stress or salt -involves the following system: Possible target for downregulation could be Bir1p (from BIR1 gene), a homolog of survivin from humans that is thought to stabilize XIAP Another possible target is AIF1, a homolog of the human AIF1 -released from mito.and travels to nucleus -interesting fact about S. cerevisiae is that they are facultative anaerobic yeast and can survive even with complete removal of mitochondria, making them an ideal system for studying PCD (Frolich- Yeast apoptosos) http://www.nature.com/embor/journal/v6/n11/full/7400514.html |
 "
"