Team:Paris/Project
From 2008.igem.org
|
Presentation of the project
SpecificationsOur project aims at constructing a sequence of genes activated sequentially in a First In First Out (FIFO) order and periodically and synchronized at population scale. To this end we implement a biological FIFO circuit in a negative feedback loop and a cell-cell communication channel. Such a setup is designed to trigger a sequence of several genes successive activations repeated periodically. Thus, it can be considered as a biological clock.
We will base our project on an already existing structure, partly fulfilling the evoked specifications: the system that leads to the production of E. coli flagella. MotivationsFIFOFirst In First Out (FIFO) systems are present everywhere from flux management or electronics to genetic networks. A queue in front of the post office works as a FIFO. More generally, it is interesting in any process that requires several steps in a defined order. FIFO behavior indeed prevents from needlessly performing the first steps while the last ones are OFF. If you want to make French fries you need to produce potatoes before you can cut them and you need to cut them before frying them. But it would be a waste to continue producing potatoes if you've already turned off the fryer. You would accumulate unprocessed intermediates ! The same goes for the bacterium flagella. To be efficient they naturally need to produce the proteins of the base first. But when you stop making flagella, the base proteins are also the first thing you need to stop producing. It has been proposed [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15186773?ordinalpos=2&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_DefaultReportPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum| (Kalir S., Alon U. 2004)] that the gene network controlling the production of E.coli flagellum behaves as a FIFO. We thus decided to use this regulatory network to implement our FIFO.
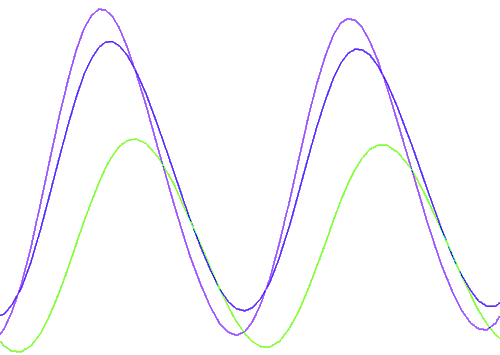
OscillationsGenetic oscillators based on the interaction of a small set of molecular components have been shown to be involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, the circadian rhythms, or the response of several signaling pathways. Uncovering the functional properties of such oscillators then becomes important for the understanding of these cellular processes and for the characterization of fundamental properties of more complex clocks. Creating an oscillating device has always been at the core of synthetic biology. There are many systems that can lead in theory to this complex behavior with different properties : number of cycles, oscillating period and robustness. Our oscillator has an original structure that has not been tested yet, based on a particular gene network called Feed Forward Loop. Engineering and tuning such complex cellular behaviors is a real challenge for synthetic biology. Synchronization
Several teams around the world worked on the synchronization of oscillations. The phenomenon of quorum-sensing, is a natural way to synchronize the expression of gene network in bacteria. We will embezzle a natural quorum sensing system to do so.
|
 "
"