|
Network Design - Part 1
Generating a FIFO sequential order of expression
A clock that would only indicate one hour, would not be very useful. The same goes for our BacteriO'clock. It is necessary that we add several distinct events in each cycle. We want to use three genes activated successively.
The easiest way to control a sequential expression of genes : the LIFO order
 The washing of dirty plates traditionally follows a LIFO order : the last plate put on the stack is the first one to be washed 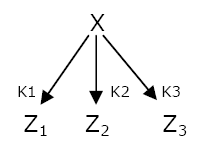 Network 1 : The Single Input Module can generate a LIFO temporal order.
The temporal order of expression that is the easiest to set up is the Last In First Out temporal order. The genetic network that generates this behavior is the Single Input Module (SIM) (Network 1). A transcription factor X activates the expression of different genes Zi. When X concentration increases, the threshold of activation Ki of the different genes Z are reached in a precise order. The expression will stop in the opposite order when X is not expressed anymore. To cut a long story short, the first gene to be switched on will be the last one to be OFF.
This order poses a real problem to us : several states of the system are redundant (Table 1). We can not accept a clock that would display twice the same hour !
The rules to generate a FIFO temporal order
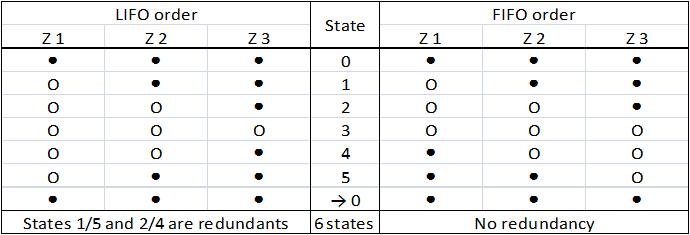 Table 1 : Comparison of the LIFO and the FIFO orders. (● : gene is OFF, O : gene is ON) In the contrary, in a FIFO order, there is no confusion possible between different states (Table 1) : they are all distincts. To generate this complex behavior, there are two major possibilities.
The simplest way to generate a FIFO : a simple cascade of genes
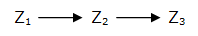 Network 2 : A cascade of gene : the simplest way to generate a FIFO behavior. The first one, the simplest, which is also the most unsophisticated, is a simple cascade of genes (Network 2). When the first gene Z1 is switched on, it activates the second gene Z2, then the third gene Z3 is turned on. When gene Z1 is turned off, Z2 is switched off first, then Z3...
This network is really simple to implement but presents several problems that makes it incompatible with our project. First of all, the cascade is not resistant to mutations : when one gene is mutated, the cascade is definitely broken. Secondly, the time scale if far too long. Each activation step would take approximately one hour. One full cycle would last almost six hours. Last but not least, the cascade is probably not very resistant to intracellular noise, it is not robust enough.
The more sophisticated way to generate a FIFO behavior : a particular Multiple Output Feed-Forward Loop
The other way to implement a FIFO is based on a logic structure called Feed Forward Loop.
↓ Click here to know more about Feed Forward Loops ↑
Definition of a FFL
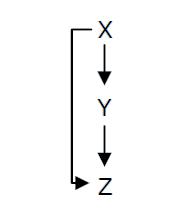 Fig. 1 : Structure of a type 1 coherent Feed Forward Loop
A Feed-Forward Loop is a genetic network composed of three nodes. This strong network motif is composed of a transcription factor X that regulates a second transcription factor, Y, and both X and Y regulate Z (Figure 1).
The different types of FFL
Depending on the type of regulations between the different nodes, we can define eight types of FFL that can be classified into two groups : coherent and incoherent FFLs. In coherent FFLs, the indirect path has the same overall sign as the direct path. The most abundant FFL is the type-1 coherent FFL (C1-FFL) (Figure 1).
The type 1 coherent Feed Forward Loop with an OR gate introduces a delay after the extinction of the signal
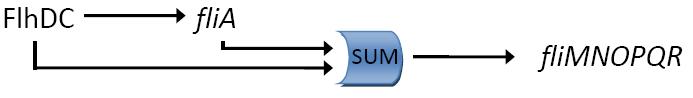 Fig. 2 : The C1-FFL with OR logic in the flagella system of E. coli. 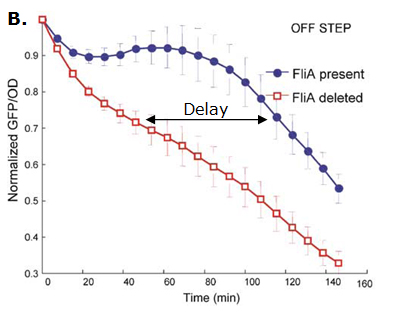 Fig. 3 : Promoter dynamics after an OFF step of X, in the presence of Y. The results are shown for the wild-type bacterium, and for a bacterium in which the gene for Fli1 was deleted from the genome. The FFL generates a delay after an OFF step of X
In addition to the signs of the edges, to understand the dynamics of the FFL, we must also know how the inputs from the two regulators X and Y are integrated at the promoter of the gene Z. Uri ALON considers that there are two biologically reasonable logic functions : "AND" logic, in which both X and Y activities are need to be high in order to turn on Z expression and "OR" logic in which either X or Y is sufficient (Figure 2).
If the input function of the promoter of the gene Z is "OR", Z is expressed when X activity is high. There is no delay following the expression of X. But when X is not expressed anymore, its concentration decreases and reach the activation threshold of Y and Z. Y is not expressed anymore but as the concentration decreases, Z is still expressed. The OR-gate C1-FFL allow the gene Z to be expressed about one more hour after the gene X is OFF. (Figure 3)
Bibliography :
- [http://www.nature.com/ng/journal/v31/n1/abs/ng881.html Shen-Orr et al. (2002)]
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14607112?ordinalpos=1&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_DefaultReportPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum Mangan et al. (2003)]
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14530388?ordinalpos=2&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_DefaultReportPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum Mangan et al. (2003)]
- [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=16729041 Kalir et al. (2005)]
|
More precisely, the genetic network is called Multiple Output FFL (Network 3). Each gene Zi is regulated by both X and Y, as in a typical FFL. X activates Zi when its concentration reaches the threshold KX/Zi. It is the same for Y and its respective thresholds.
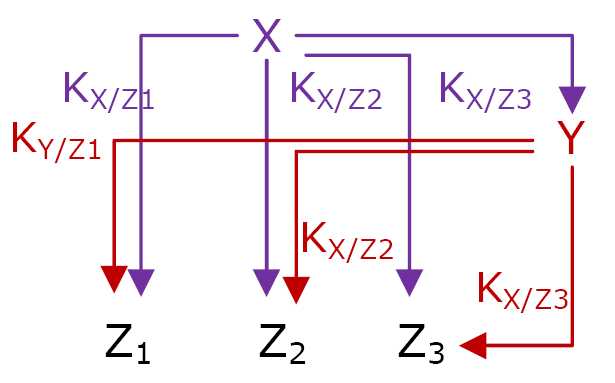 Network 3 : Multiple Output FFL is the logic structure that permit FIFO behavior. The thresholds must be ordered is a precise way : K X/Z1 < K X/Z2 < K X/Z3 and K X/Z1 > K X/Z2 > K X/Z3
All the MO FFL do not behave according to the FIFO order, three conditions are necessary and sufficient.
- The input function for each gene Zi must be a OR or a SUM gate.
- To have the order of expression Z1, Z2 and then Z3 at the switching ON, the thresholds must be ordered like this :
KX/Z1 < KX/Z2 < KX/Z3
- To have the FIFO order, Z1 must be the first gene to be switched OFF when X is no more expressed. When X is not expresses anymore, its concentration decreases. The threshold KX/Z1 will be reached after the thresholds KX/Z2 and KX/Z3. As Y is still expressed when X decreases, its own concentration will decrease with a delay. To have a FIFO, Y concentration must reach KY/Z1 before KX/Z2 and KX/Z3. The necessary order must be :
KY/Z1 > KY/Z2 > KY/Z3
This network has several advantages compared to the cascade. It is more resistant to mutations : if gene Z1 is mutated, genes Z2 and Z3 still behave as they should do. This is particularly interesting if we need more than three genes. The MOFFL is more robust concerning intracellular noisy fluctuations of concentration. The temporal expression of genes is more tunable : the expression of gene Z2 can be fully activated even if Z1 is not concentrated enough.
Implementation of our FIFO
Now that the necessaries and sufficient conditions have been depicted, we can start to describe our FIFO. Rather than designing it from scratch we decided to look in nature where we found and adopted the flagella which then inspired us further.
↓ Click here to know more about E. coli flagella. ↑
Description of the genetic pathway that lead to flagella assembly
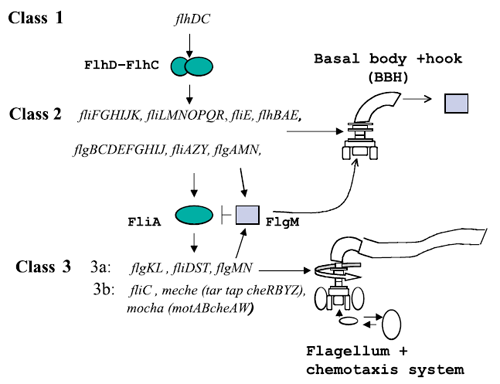 Figure 1 : The genetically defined hierarchy of the flagellar operons in Escherichia coli. The construction of E. coli flagellar system is organized into a complex hierarchy. The different parts of the flagella are successively assembled parts by parts. This architecture is also present in the network of genes that contributes to its set-up.
A global transcription factor FlhDC activates the synthesis of the flagella. This class 1 gene encodes a protein that activates the expression of class 2 genes. Those genes lead to the construction of the basal body of the flagella and its hook. Then FliA, a protein coded by a class 2 gene activates, with FlhDC to the expression of class 3 genes (Figure 1).
The expression of the flagellar genes is precisely ordered
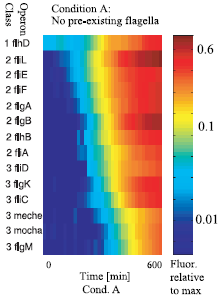 Figure 2 : The sequential expression of flagellar genes The observed order correponds to the spatial position of the gene products during flafellar motor assemblu, going from the cytoplasmic to the extracellular sides.
A quantitative blueprint of the dynamics of the flagella gene network
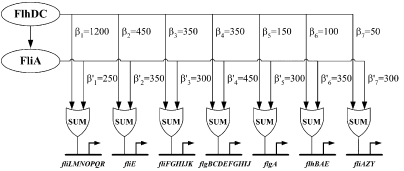 Figure 3 : Quantitative blueprint of the dynamics of class 2 genes of the flagella gene network. β is the activation coefficient corresponding to a transcription factor and a promoter (unit : GFP/OD).
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15186773?ordinalpos=2&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_DefaultReportPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum| Kalir et al. (2004)] evaluated the strength of the interactions between the different transcription factors fliA and flhDC and the class 2 promoters. They established a quantitative blueprint, considering the strength of the interactions and the functions that integrate multiple input (Figure 3). The structure of this network is typically a Multiple Output FFL, each class 2 gene is regulated by both flhDC and fliA, which is itself regulated by flhDC. This network is the logic circuit that can generate a FIFO behavior.
They determined that the input function for fliL promoter is a SUM gate in relation to FliA and FlhDC.
It means that: Promoter_Activity([FlhDC],[FliA]) = Promoter_Activity([FlhDC],0) + Promoter_Activity(0,[FliA])
The existence of a SUM input function for the other promoters has not been demonstrated but Uri ALON and his team assume that all the class 2 promoters have the same behavior. This is the first condition to create a FIFO.
The coefficients of activation for fliL, flgA and flhB are ordered in the right way to behave as a FIFO :
β1<β5<β6 and β'1>β'5>β'6
The dynamics is easily tunable, which is a great tool for engineering
The model suggests that, in order to change the response time, one can change the numbers on the arrows. For the earliest promoter, fliL, decreasing β1 should make the rise time longer and the maximal expression lower compared to the wild-type promoter. To experimentally change β1, Shiraz KALIR and Uri ALON inserted point mutations in the FlhDC binding site of the fliL promoter. Those mutations made the promoter activity later and weaker.
Bibliography
- [http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/abstract/292/5524/2080| Kalir et al. (2001)]
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15186773?ordinalpos=2&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_DefaultReportPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum| Kalir et al. (2004)]
|
Previous step : Project Description
Next step : Network Design Part 2 : Oscillations
|
 "
"









