From 2008.igem.org
Part I Mutation Model
Hypothesis
- The mutation efficiency from the initial gene to the target gene should remain a continuous curve along reproduction, or along time. Here we discrete the mutation rate to be linear function according to the replication time (), which in fact create several discontiguous point.
- DNA lesion repair rate appears high enough in replication than other cell activities, so that the DNA lesion repair rate can be conformed to background mutations except in replication process.
- The whole yeast is large enough to obey the statistics rules
Model Construction
- Probability Model
For each DNA sequence status, we take down a probability matrix for the coding sequence, which gives out each base appearance possibility on every site. The structure on each site is 5*1 matrix,(Pa,Pt,Pc,Pg,Pu), and ΣP=1. Therefore, the whole sequence status is recorded as 5*length matrix.E.g. For the Gal4 DNA, with a length of 2646, one status is a 5*2646 matrix.
- Scanning Model
The hotbox appearance rate on a specific site i is calculated as below.
W: a, t; R: a, g; H: a, c, g;
Hotbox appearrance rate PH=PW(i-2)PR(i-2)PC(i-2)PH(i-2), and here (i) refers to the site i.
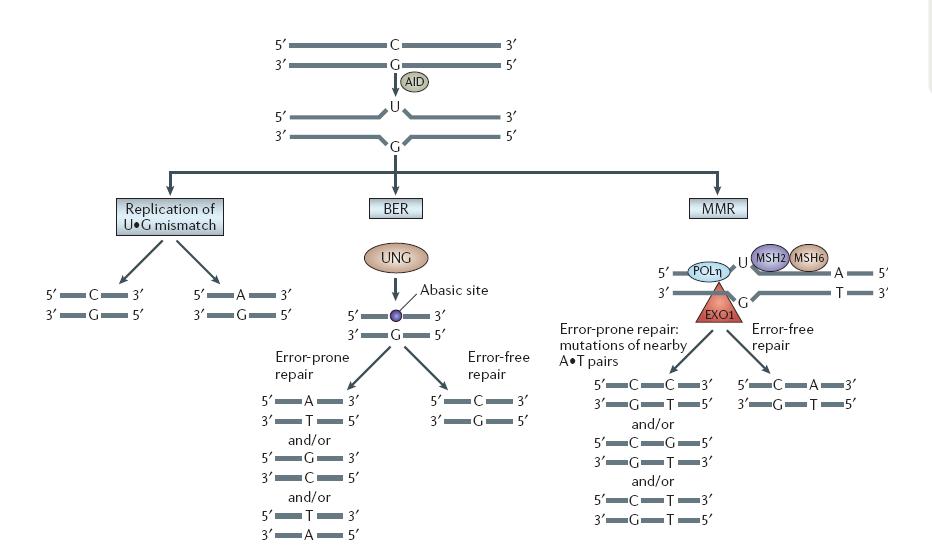
- Model on DNA lesion repair
As reviewed by the paper, the U:G mismatch DNA lesion will be repaired in three pathways.
| VH Odegard, DG Schatz. Targeting of somatic hypermutation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006 Aug;6(8):573-83
|

 "
"