x
The two constructs that we designed are detailed bellow. KDP is the potassium importer and GluR0 is the glutamate gated potassium channel. Details of their construction can be found here:
KDP
GluR0
KdpF-C Biobrick- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K090003 BBa_K090003]=
Gene Selection
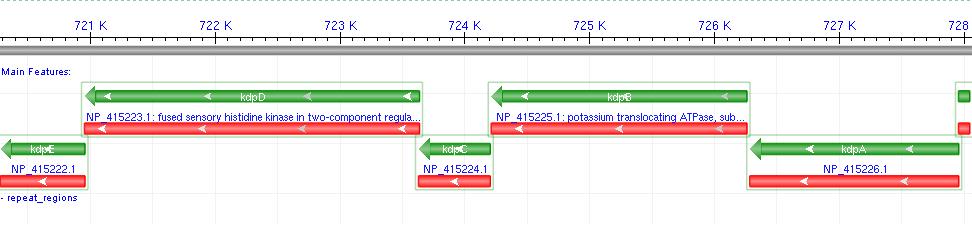
- Kdp is a well documented P-Type K+ ATPase found naturally in E.coli, used to actively pump ions into the cell.
- It consists of a 6-gene operon: F,A,B,C,D,E Where F-C are the functional membrane protein subunits, and D-E comprises a bacterial 2-component regulatory system.
- Literature shows that Kdp acts as a high-affinity transport system, and works most effectively at low external potassium concentrations, where a change in ion flux would be most likely to produce a measurable voltage difference.
- The D-E 2-component system consists of a membrane protein turgidity sensor and a transcription factor. It controls Kdp operon expression in vivo, by reducing gene expression when turgor is high.
- Since we wish to over-express Kdp, we decided not to include the regulatory system in our biobrick. (Osmotic buffering would be used instead.)
Amplification from E.coli MG1655
- This was performed via PCR amplification of the genome template using the following primers:
-Forward: ATAT GAATTC ATAT TCTAGA TGAGTGCAGGCGTGATAACCGGCGTATT
EcoRI XbaI
-Reverse: CTCT CTGCAG CTCT ACTAGT TTATTCATCAAGTTTATCCAGCGCCAGAT
PstI SpeI
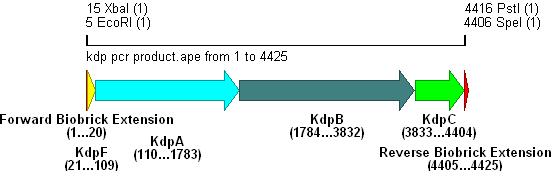
- Primer overhangs incorporated the biobrick prefix and suffix into the section, restriction sites shown in bold .
- The result of this PCR is shown below:
Integration into Vector
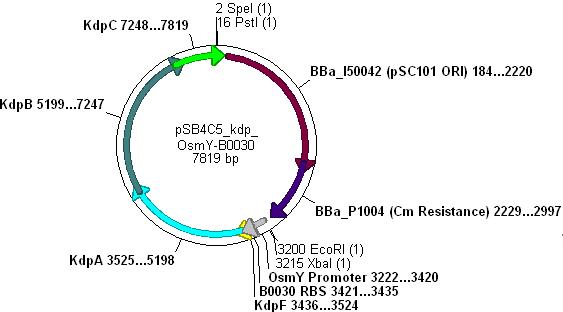
- The vector used was low copy-number plasmid [http://partsregistry.org/Part:pSB4C5 pSB4C5], with chloramphenicol resistance and a death gene as selection markers.
- Kdp PCR product and pSB4C5 were both cut with EcoRI & SpeI, (vector backbone was dephosphorylated to prevent circularisation) then ligation into the vector can occur as shown.
- . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
- Note: pSB4C5_Kdp biobrick plasmid has no promoter/RBS and so Kdp is not expressed in transformants.
Promoter+RBS Biobrick
Promoter and RBS Selection
Promoter
- The promoter chosen for use with Kdp was OsmY [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J45992 (Part BBa_J45992).]
- It is a stationary phase promoter, and since we require high cell densities in our final "voltage measurement" medium, we want Kdp to only be expressed in stationary phase.
- This will reduce the metabolic and osmotic stress on dividing cells in exponential phase.
Ribosome Binding Site
- Three different strength RBSs were investigated, [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0030 B0030], [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0031 B0031] and [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0032 B0032].
- B0030 is the strongest(15bp length), B0031 medium(14bp) and B0032 weakest(13bp).
- Investigating three will help us determine the optimum levels of Kdp expression.
Amplification from E.coli MG1655
- These parts were extracted using PCR from the Registry of Standard Biological Parts. However, the RBS biobricks are so small that we built their sequences into the reverse primers.
- The primer sequences used are:
-Forward: CTAT GAATTC ATAT TCTAGA GCTGGCACAGGAACGTTATCC (All OsmY-RBS constructs)
EcoRI XbaI
-B0030 Reverse: CGCG CTGCAG CTCT ACTAGT (TTTCTCCTCTTTAAT)TTGTTAAATATAGA
PstI SpeI B0030
-B0031 Reverse: CTCT CTGCAG CTCT ACTAGT (GGTTTCCTGTGTGA)TTGTTAAATATAGAT
PstI SpeI B0031
-B0032 Reverse: CTCT CTGCAG CTCT ACTAGT (CTTTCCTGTGTGA)TTGTTAAATATAGATCA
PstI SpeI B0032
- PCR with these primers creates three different promoter-RBS biobrick parts (OsmY-B003x):
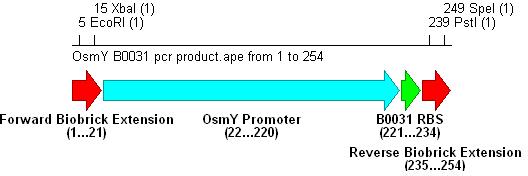
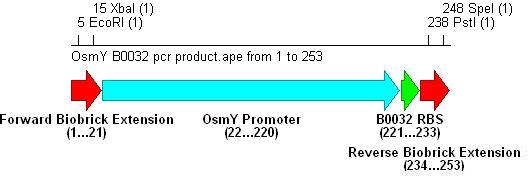
Integration into Vector
- The vector used was low copy-number plasmid [http://partsregistry.org/Part:pSB4C5 pSB4C5], with chloramphenicol resistance and a death gene as selection markers.
- OsmY-B003x and pSB4C5 were both cut with XbaI & SpeI, (vector backbone was dephosphorylated to prevent circularisation) then ligation into the vector can occur as shown:
- . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
- Note: This promoter-RBS construct did not cause unwanted transcript problems because there are many double terminators scattered throughout the pSB4C5 backbone.
Combination of Kdp, OsmY and B003x - [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K090004 BBa_K090004]
- This will create a functional biobrick plasmid in which Kdp is overexpressed only in stationary phase of growing cells.
- Cut pSB4C5-Kdp with XbaI and PstI
- Cut pSB4C5-OsmY-B003x with PstI first, then SpeI, in order to make sure Pst cuts correctly.
- Ligation will form the following functional plasmid:
GluR0 Biobrick- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K090002 BBa_K090002]
Gene Selection
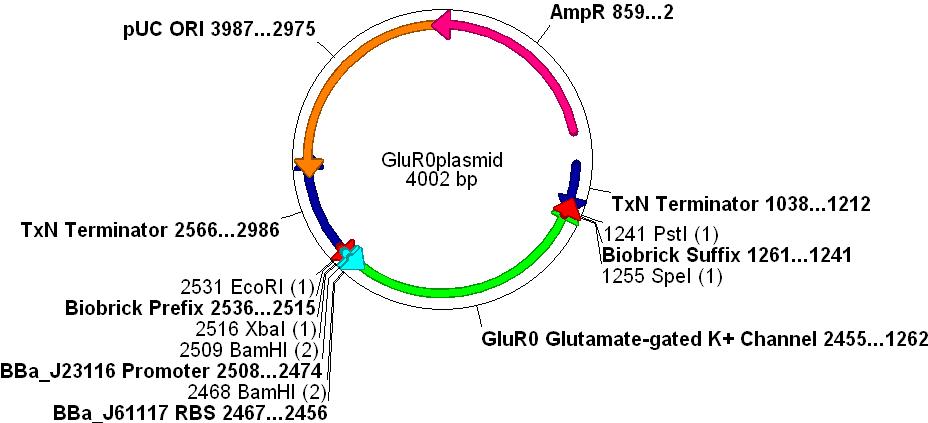
- In order to create a measurable voltage change when a chemical was "recognised" we decided to use an ionotropic ligand-gated potassium efflux channel that binds glutamate. This also simulates the action of glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the CNS.
- The gene chosen comes from the cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. This species is gram negative (similar to E.coli) and is used as a paradigm for evolutionary research concerning the AMPA receptor proteins.
- GluR0 is a well characterised glutamate-gated K+ membrane channel, which has a considerable degree of structural and functional homology to rat neurone GluR2 AMPA receptors, see the paper [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v402/n6763/full/402817a0.html Functional Characterisation of a Glutamate-gated Potassium Channel]
DNA Synthesis
- The protein sequence was obtained via NCBI from the [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?tool=portal&db=protein&term=&query%5Fkey=2&dopt=gp&dispmax=20&page=1&qty=1&WebEnv=0Z1aMb1oSyT%5FAsbY%5Fe8SHH5%5FIGnme2UYVwupBbQ8pXgSmignz7xFMxGxDxnS%5FdHJl5fpNJ1RyQVTXT3f%404A8B168688057500%5F0127SID&WebEnvRq=1 Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 genome].
- The gene sequence could not be directly used because of codon optimisation problems (Synechocystis uses many codons that are "rare" in E.coli"
- The protein sequence was back-translated to DNA using GeneDesigner™ and codons were assigned using the E.coli usage table.
- The promoter [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J23116 BBa_J23116], RBS [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J61117 BBa_J61117] and Biobrick prefix and suffix sequences were added to the design.
- Finally, unwanted restriction sites within the gene(EcoRI, XbaI, SpeI and PstI) were manually removed by selecting alternative codons for any given amino acid.
- The gene was synthesised and sequenced by DNA2.0 into one of their standard vectors.
x