Team:BrownTwo
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→A Genetic Limiter Circuit in S. cerevisiae) |
(→A Genetic Limiter Circuit in S. cerevisiae) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==A Genetic Limiter Circuit in ''S. cerevisiae''== | ==A Genetic Limiter Circuit in ''S. cerevisiae''== | ||
| - | <br> | + | |
| - | + | ||
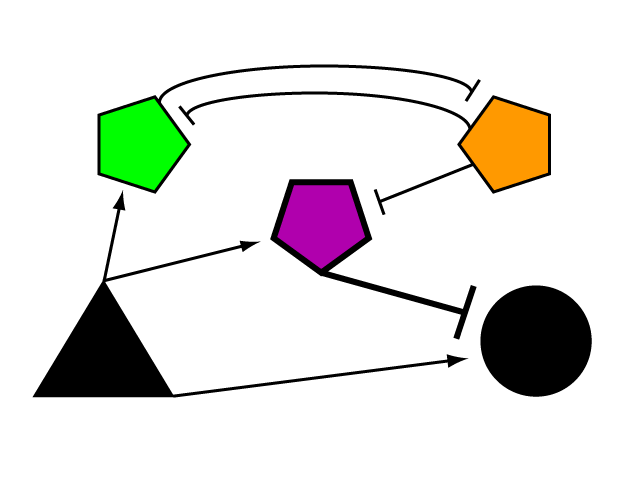
| + | [[image:Glyph.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | <br><p> | ||
| + | We have designed a modular genetic circuit to limit the expression level of a gene of interest to a user-defined, tunable threshold. The limiter network reacts to the transcription of an endogenous gene within each cell, entering a regulatory state only where and when the rate of transcription lies beyond an acceptable range of activity. Along with its potential therapeutic utility, we offer our device as a foundational tool for researching gene expression in a eukaryotic model. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <center>'''''This page is best viewed with any browser but Internet Explorer.''''' | ||
| + | </center> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:42, 30 October 2008
A Genetic Limiter Circuit in S. cerevisiaeWe have designed a modular genetic circuit to limit the expression level of a gene of interest to a user-defined, tunable threshold. The limiter network reacts to the transcription of an endogenous gene within each cell, entering a regulatory state only where and when the rate of transcription lies beyond an acceptable range of activity. Along with its potential therapeutic utility, we offer our device as a foundational tool for researching gene expression in a eukaryotic model.
|
 "
"