Team:Minnesota/ProjectTimeBomb
From 2008.igem.org
| Home | Team Time Bomb Homepage | Team Page | Project Page | Parts Submitted to the Registry | Team Notebook |
|---|
Overall project
The process of in situ Bioremediation would be aided through the use of microorganisms that undergo synchronized cell death. Bioremediation relies on microorganisms' enzymatic pathways to break down hazard chemicals in the environment. However, in order to protect the environment from the release of a foreign population of microorganisms, most contaminants have to be excavated or pumped off-site (ex situ) before the proper microogranisms can be applied. The transport of contaminants makes ex situ bioremediation just as expensive as the burn or bury methods of waste removal. Although if the remediating microorganisms were engineered to clean up until the contaminant was removed, and then collectively die, their impact on native populations could be reduced significantly.
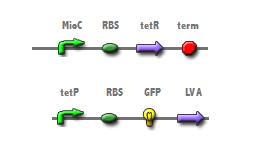
To achieve synchronized apoptosis after a set number of generations we first had be able to link cell divisions to a predictable buildup of toxin. This required that the origin of replication (OriC) would have to be cloned out of E. coli; but to be functional, it would still need to retain the proper binding site spacing and restriction regions around the OriC promoter.
Project Detail
The protein DnaA is required for cell replication and the cell cycle dependent repression of mioC. Replication of the bacterial chromosome is triggered through the highly conserved binding of DnaA proteins to a region called the oriC. There are several binding sites for DnaA within, upstream, and downstream of the oriC region which induce replication during mitosis. (1) However, four of these DnaA binding sites are also found in the promoter of the gene mioC. (2) (3) In this case, the binding of DnaA has been found to repress the promoter of mioC during mitosis. (3)
The cell cycle dependent expression of the mioC promoter should accurately count cell division when linked to a reporter. The insertion of mioC into a plasmid upstream from a tetracycline repressor will allow for the expression of the repressor during interphase; at which time, tetracycline represses the tetracycline promoter of construct 2.
 "
"