|
Step 1
|
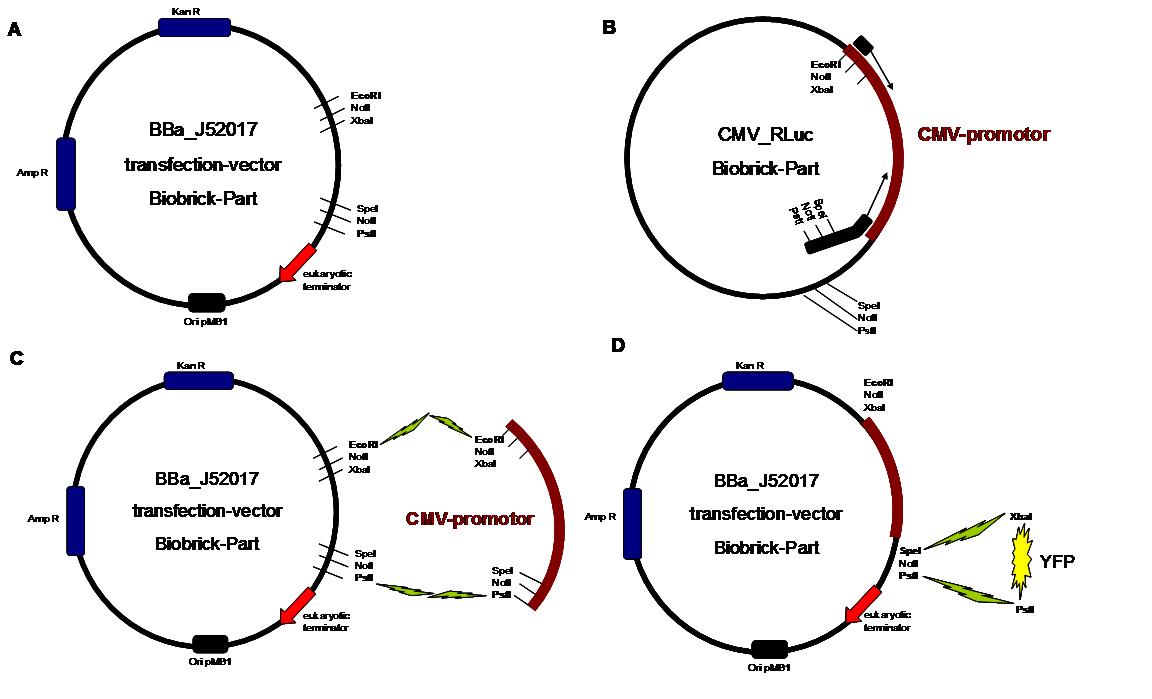
Vector
digestion: EcoRI + PstI
|
Insert
digestion: EcoRI + PstI
|
|
|
BBa-J52017
|
_CMV-promotor
|
|
Step
2
|
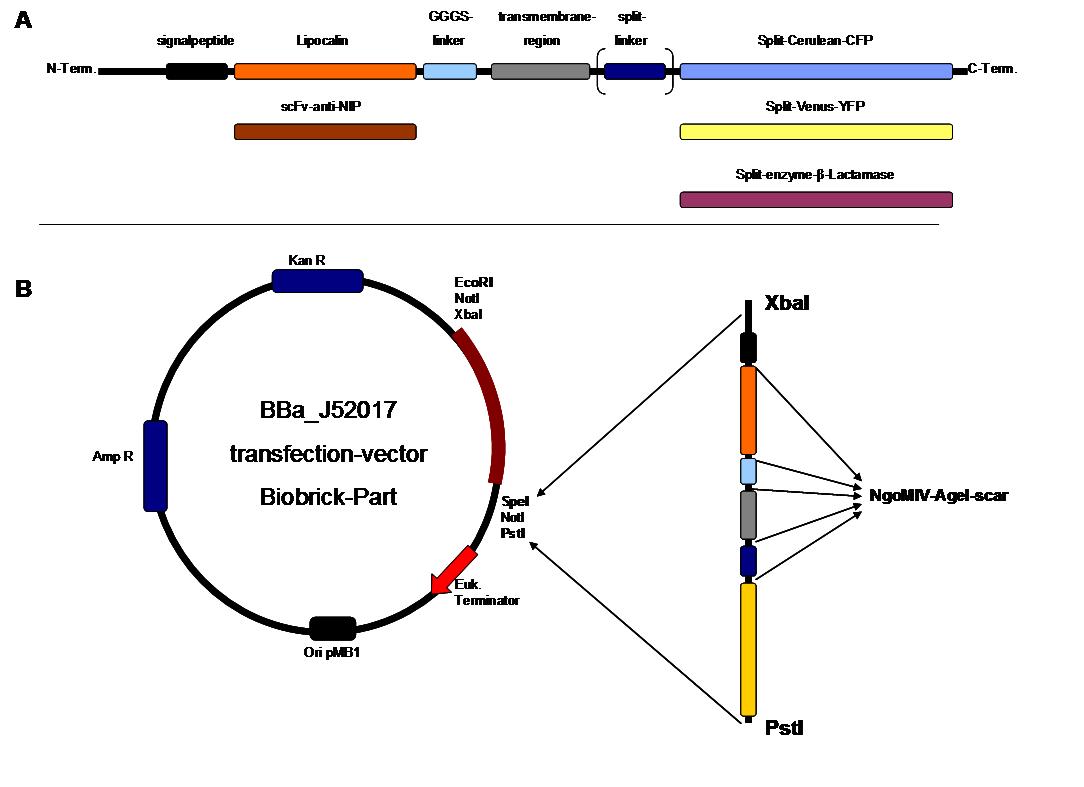
Vector
digestion: AgeI+SpeI
|
Insert
digestion: NgoMIV+SpeI
|
|
|
pMA-BBFR
_ SPLIT-Linker
|
C-YFP
|
|
|
C-CFP
|
|
Step
3
|
Vector
digestion: AgeI+SpeI
|
Insert
digestion: NgoMIV+SpeI
|
|
|
pMA-BBFR
_egfR-Tm
|
_ N-β-Lactamase
|
|
|
_ C-β-Lactamase
|
|
|
_ SPLIT-Linker_ C-YFP
|
|
|
_ N-YFP
|
|
|
_ SPLIT-Linker_ C-CFP
|
|
|
_ N-CFP
|
|
|
_ BB058 (Luciferase)
|
|
|
_ BB057 (Luciferase)
|
|
Step
4
|
Vector
digestion: AgeI+SpeI
|
Insert
digestion: NgoMIV+SpeI
|
|
|
pMA-BBFR
_SP
|
_scFv-anti-NIP
|
|
|
_ Lipocalin
|
|
Step
5
|
Vector
digestion: AgeI+SpeI
|
Insert
digestion: NgoMIV+SpeI
|
|
|
pMA-BBFR
_SP_ scFv-anti-NIP
and
pMA-BBFR-+SP_ Lipocalin
|
_GGGS-linker (produced by Klenow fill in)
|
|
Step
6
|
Vector
digestion: AgeI+SpeI
|
Insert
digestion: NgoMIV+SpeI
|
|
|
pMA-BBFR
_SP_ scFv-anti-NIP _ GGGS-Li
and
pMA-BBFR
_ SP_ Lipocalin _
GGGS-Li
|
_
egfR-Tm _ N-β-Lactamase
|
|
|
_
egfR-Tm _ C-β-Lactamase
|
|
|
_
egfR-Tm _ SPLIT-Linker_ C-YFP
|
|
|
_
egfR-Tm _ N-YFP
|
|
|
_
egfR-Tm _ SPLIT-Linker_ C-CFP
|
|
|
_
egfR-Tm _ N-CFP
|
|
|
_
egfR-Tm _ BB058 (Luciferase)
|
|
|
_
egfR-Tm _ BB057 (Luciferase)
|
|
Step
7
|
Vector
digestion:
SpeI + PstI
|
Insert
digestion: XbaI + PstI
|
|
|
BBa-J52017_CMV
|
_SP_ scFv-anti-NIP_GGGS-Li_egfR-Tm_N-β-Lactamase
|
|
|
_ SP_ scFv-anti-NI _GGGS-Li_ egfR-Tm_C-β-Lactamase
|
|
|
_ SP_ scFv-anti-NIP_GGGS-Li_
egfR-Tm_SPLIT-Linker_C-YFP
|
|
|
_ SP_ scFv-anti-NIP_GGGS-Li_ egfR-Tm_N-YFP
|
|
|
_ SP_ scFv-anti-NIP_GGGS-Li_
egfR-Tm_SPLIT-Linker_C-CFP
|
|
|
_ SP_ scFv-anti-NIP_GGGS-Li_ egfR-Tm_N-CFP
|
|
|
_ SP_ scFv-anti-NIP_GGGS-Li _ egfR-Tm_BB058 (Luciferase)
|
|
|
_ SP_ scFv-anti-NIP_GGGS-Li _ egfR-Tm_BB057 (Luciferase)
|
|
|
_ SP_ Lipocalin _GGGS-Li_ egfR-Tm_N-β-Lactamase
|
|
|
_ SP_ Lipocalin _GGGS-Li_ egfR-Tm_C-β-Lactamase
|
|
|
_ SP_ Lipocalin _GGGS-Li_
egfR-Tm_SPLIT-Linker_ C-YFP
|
|
|
_ SP_ Lipocalin _GGGS-Li_
egfR-Tm_N-YFP
|
|
|
_ SP_ Lipocalin _GGGS-Li_
egfR-Tm_SPLIT-Linker_ C-CFP
|
|
|
_ SP_ Lipocalin _GGGS-Li_
egfR-Tm_N-CFP
|
|
|
_ SP_ Lipocalin _GGGS-Li__ egfR-Tm _ BB058 (Luciferase)
|
|
|
_ SP_ Lipocalin _GGGS-Li__ egfR-Tm _ BB057 (Luciferase)
|
 "
"