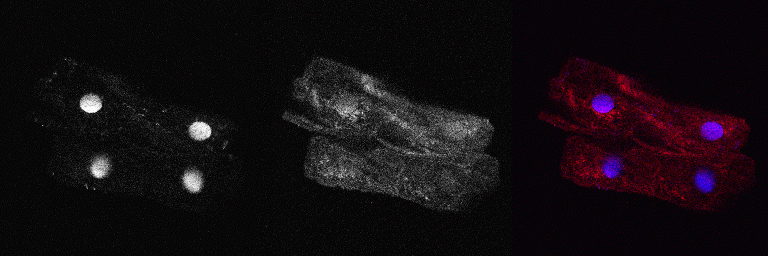From 2008.igem.org
Photo Gallery- Microscopy
Here you get an impression on what the pubils explored in the microscopy station. [ back to previous page ]
Cells taken from the oral mucosa are stained with Hoechst and Lysotracker Red in salt-buffer (Krebs-Henseleit). Hoechst is a blue fluorescend dye intercalating into the minor groove of the DNA, thus visualizing the nucleus. Lysotracker Red consists of a red fluorophore coupled to a weak base that accumulates in acidic organelles like lysosomes. A Leica TCS SP5 confocal microscope is used for image aquisition.
 Cells of the oral mucosa covered with bacteria (Hoechst stain) |  Cells of the oral mucosa focused to the nucleus (Hoechst stain) |
 Montage: Cells of the oral mucosa covered with bacteria. Blue color indicates the nucleus and bacterial DNA, Red color stains acidic compartments and gives a diffuse background in the cytosol. |  Cells of the oral mucosa focused to the nucleus. Blue color indicates the nucleus and bacterial DNA, Red color stains acidic compartments and gives a diffuse background in the cytosol. |
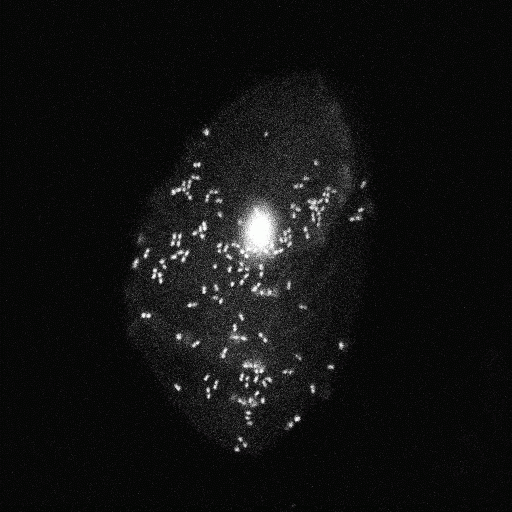
 Group 1: Hoechst stain of cells from the oral mucosa | 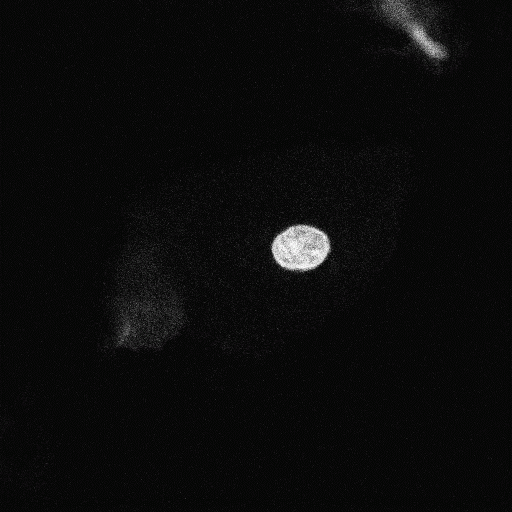 Group 2: Hoechst stain of cells from the oral mucosa |
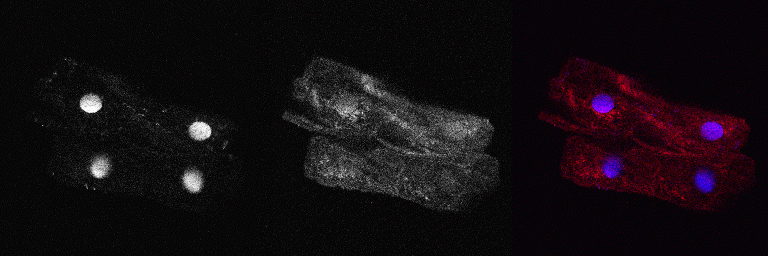 Montage group 1: Blue color indicates the nucleus and bacterial DNA, Red color stains acidic compartments and gives a diffuse background in the cytosol. |  Montage group 2: Blue color indicates the nucleus and bacterial DNA, Red color stains acidic compartments and gives a diffuse background in the cytosol. |
 Group 3: Hoechst stain of cells from the oral mucosa |  Group 3: Hoechst stain of cells from the oral mucosa |
 Montage group 3: Blue color indicates the nucleus and bacterial DNA, Red color stains acidic compartments and gives a diffuse background in the cytosol. |  Montage group 3: Blue color indicates the nucleus and bacterial DNA, Red color stains acidic compartments and gives a diffuse background in the cytosol. |
[ back to previous page ]


 "
"