Team:Montreal/Project
From 2008.igem.org
| Home | The Team | The Project | Parts | Notebook | Modeling | Links | Sponsors |
|---|
Contents |
Taming The Repressilator
Building on previous years of research, the McGill University iGEM team intends to construct a set of Biobricks that will maintain synchronous oscillations in a large population of cells. If accomplished, our theorists and experimentalists will cooperate to refine this system using various modifications to further our understanding of biological clocks and their functioning.
Project Objectives
Experimental
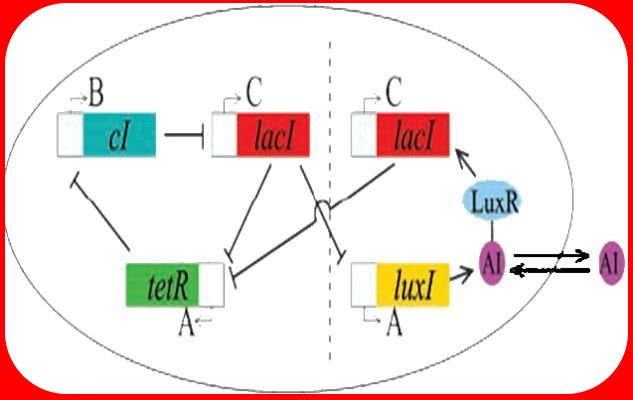
To create our functional bacteria, we intend to transform a line of MC4100 E. coli cells used by Elowitz with two plasmids. The first plasmid will contain the Repressilator (λcI, TetR and LacI), described in his 2000 paper. The second plasmid will be a triple-ligation of the I-like bio-brick, the J40001 bio-brick and the Elowitz reporter (TetR, YFP).
If successful, we intend to observe oscillating fluorescence with large amplitudes in microscopy and spectrophotometry experiments. Using three individual filters, we can microscopically observe the oscillations of individual components by the three fluorescent proteins (ECFP, GFP and RFP) embedded in the system.
Parts
- The Repressilator
- J40001
- I-like brick: gene synthesized for use with our system. Somewhat similar to BBa_I15004
plac - rbs - luxI - RFP - STOP - J23119 - rbs - luxR - STOP
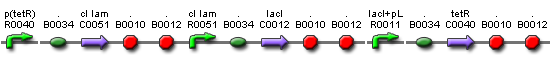
- Plasmid A: λcI + TetR + LacI (Elowitz Repressilator) Ampicillin Resistant
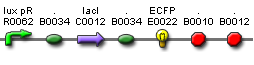
- Plasmid B: I-like + J40001 + TetR/YFP (Elowitz Reporter) Kanamycin Resistant
Modeling
The modeling effort attempts to simulate a repressilator network using a system of coupled differential equations. The repressilator itself is modelled as a loop of three proteins which inhibit each other's growth. Each cell in the network contains a repressilator, and the cells communicate amongst themselves by exchanging an autoinducer molecule, which feeds back the repressilator loop. The simulation is currently done using Mathematica, along with the xCellerator and NDelayDSolve packages.
The model is assuming continuous levels of the different proteins, as well as a continuous spatial distribution of these proteins. It attempts to take into account lab issues such as depletion of the autoinducer molecule and leakage by introducing a time delay in the equations and by considering sparse distributions of cells within the field of view.
Once the model is set up, the goal is to explore different cell configurations and observe how the behaviour of the repressilator changes as a result. In particular, we are interested in the concentration of the auto-inducer molecule as a function of time, their period of oscillation, the speed with which the cells synchronise (if they do) or the phase difference between various clusters of cells (if they don't).
Future Applications
Pacemaking Technology
Once of the better known sinusoidal oscillators in the human body are the cells of the sinoatrial node of the heart that establish a regular rhythm of action potentials that propagate throughout the atria and ventricles to generate beats. While current artificial pacemakers focus primarily on re-establishing this rhythm by generating electrical potentials, a biological alternative could prove more effective and less invasive than its mechanical counterpart with further research.
Continuous Cultures in Industrial Bio-Reactors
A common problem in bio-reactors used by pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies results from difficulties in growing cells in continuous cultures due to various complications in recycling nutrients and draining metabolites. An effectively oscillating system could reduce the reliance on current fed-batch systems by allowing more effective cycles of cell growth and protein expression.
Biological Drug Delivery
With biological alternatives now being increasingly explored as mechanisms of delivering therapeutics, a functionally oscillating system could prove invaluable to tailoring drug regimes to specific systems. Innumerable biological processes function in rhythmic on/off switches and being able to control the release of certain cellular components to such a schedule may permit more effective treatment.
Past McGill iGEM Projects
2006 & 2007
The two-gene intercellular oscillatory system ([http://www.utm.utoronto.ca/~mcmillen/ McMillen] [http://www.pnas.org/cgi/reprint/99/2/679.pdf 2002]) examined in past projects developed irregular, triangular-shaped oscillation curves over extended periods of time. In an effort to improve the consistency and regularity of the oscillations, the Repressilator will be used. The system in theory should have better long-term fidelity in oscillation patterns and develop a more natural sinusoidal oscillatory pattern.
 "
"