Team:KULeuven/Model/Cell Death
From 2008.igem.org
(→Extensions to previous system) |
m (→Extensions to previous system) |
||
| Line 159: | Line 159: | ||
===Extensions to previous system=== | ===Extensions to previous system=== | ||
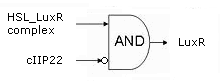
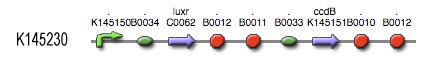
| - | During the summer we switched from the above system to a new one which you can see just below, take a look at this figure as it will help you understand the regulation that is present. This new system has a few novelties. First of all, transcription begins at a new hybrid promoter we made: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K145150 '''BBa_K145150''']. This promoter is repressed by c2 P22, which is produced by the memory in the OFF state, making premature activation and cell death impossible. Besides this repression, the promoter is activated by the HSL-LuxR complex originating from a previously activated timer. The promoter behaves as shown schematically below. | + | * During the summer we switched from the above system to a new one which you can see just below, take a look at this figure as it will help you understand the regulation that is present. This new system has a few novelties. First of all, transcription begins at a new hybrid promoter we made: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K145150 '''BBa_K145150''']. This promoter is repressed by c2 P22, which is produced by the memory in the OFF state, making premature activation and cell death impossible. Besides this repression, the promoter is activated by the HSL-LuxR complex originating from a previously activated timer. The promoter behaves as shown schematically below. |
[[Image:Hybrid_promotor.PNG|center]] | [[Image:Hybrid_promotor.PNG|center]] | ||
| - | Second, LuxR is now no longer constitutively produced but is placed behind the beforementioned hybrid promoter. This construction mimicks more closely the natural system where LuxR is upregulated when a threshold amount of HSL is present. Plus it also increases the time it takes to activate ccdB, lengthening the timer. The system will now auto-activate if enough HSL is present and the memory is in the ON state. | + | * Second, LuxR is now no longer constitutively produced but is placed behind the beforementioned hybrid promoter. This construction mimicks more closely the natural system where LuxR is upregulated when a threshold amount of HSL is present. Plus it also increases the time it takes to activate ccdB, lengthening the timer. The system will now auto-activate if enough HSL is present and the memory is in the ON state. |
| - | Third, the ccdB coding region is also downstream of the hybrid promoter and is thus also subject to the regulation explained above; c2 P22 repression and HSL-LuxR auto-activation. One difference is that the polymerase must first read through a bad terminator with about 60% efficiency before reaching this coding region. Another difference is in the ribosome binding sites preceding both coding regions. Where LuxR can be translated from a RBS with a relative efficiency of 1.00, the ccdB frame can only be read from a 0.01 efficiency RBS. | + | * Third, the ccdB coding region is also downstream of the hybrid promoter and is thus also subject to the regulation explained above; c2 P22 repression and HSL-LuxR auto-activation. One difference is that the polymerase must first read through a bad terminator with about 60% efficiency before reaching this coding region. Another difference is in the ribosome binding sites preceding both coding regions. Where LuxR can be translated from a RBS with a relative efficiency of 1.00, the ccdB frame can only be read from a 0.01 efficiency RBS. |
===Describing the system=== | ===Describing the system=== | ||
Revision as of 07:39, 2 September 2008
Contents |
Cell Death
Position in the system
The Cell Death subsystem receives input from two other subsystems, namely:
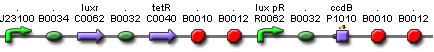
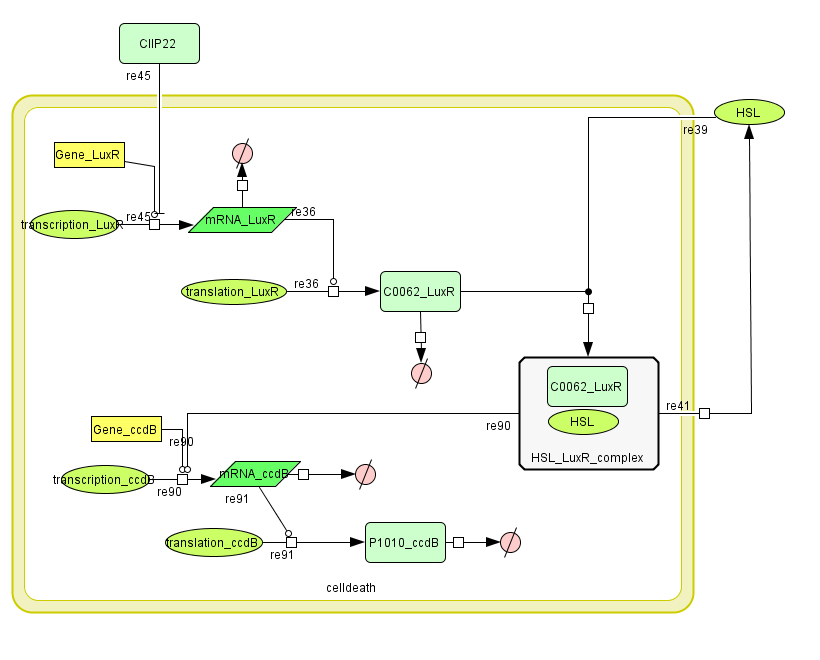
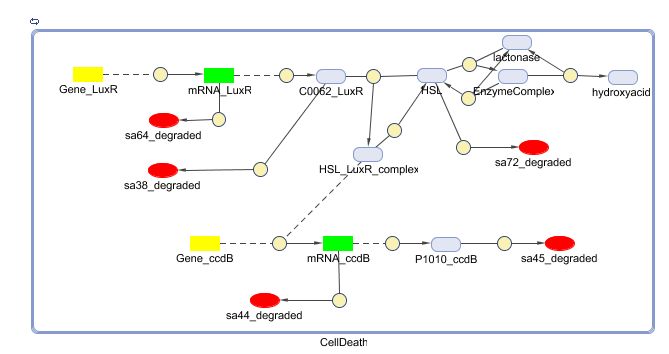
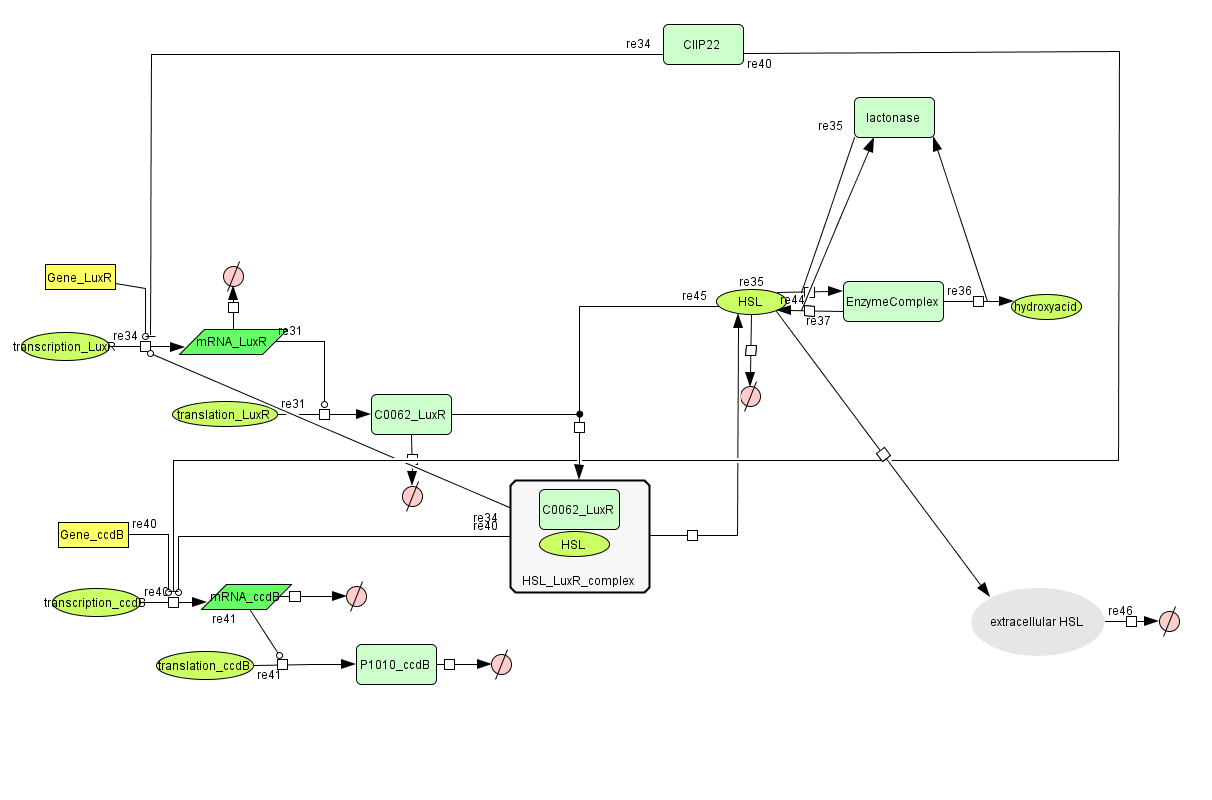
LuxR is the component repressing the regulation of CcdB, the toxic product causing cell death. There the LuxR production is constitutive, no protein controls the gene regulation of LuxR, but the amount of LuxR available to repress the transcripion of the CcdB gene is controlled by HSL (Homoserine lactone).
If the inverter subsystem produces HSL (occurs when no light is detectable), this will forms a complex with LuxR. This will diminish the amount of LuxR available to repress the CcdB transcription and initiate cell death. When waiting long enough the amount of HSL becomes critical.
If however the pulse generator becomes active (by the filter), it will produce a pulse of lactonase, which will then bind to the HSL, reacting to an hydroxy-acid. As opposed to HSL, this hydroxy-acid will no longer form a complex with LuxR. This increase in LuxR lowers the CcdB production. The challenge is to generate a pulse of lactonase high enough to neutralise all HSL present in the cell.
Describing the system
ODE's
Parameters
Remark: update parameters to repressive promotor
| Name | Value | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Degradation Rates | |||
| dLuxR | 0.0010 s-1 | ||
| dLuxR_HSL | 0.0010 s-1 | complex of HSL and LuxR degrades, giving back HSL | |
| dRNA_LuxR | 0.00227 s-1 | [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/picrender.fcgi?artid=124983&blobtype=pdf link] | |
| dCcdB | 7.7E-5 s-1 | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8022284?dopt=abstract link] | |
| dRNA_CcdB | 0.00231 s-1 | [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/picrender.fcgi?artid=124983&blobtype=pdf link] | |
| dHSL | 1.02E-6 s-1 | [http://aem.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/71/3/1291 link] | |
| Association/Dissociation/Reaction Rates | |||
| kass (HSL+LuxR) | 1E6 s-1 | association rate of HSL with LuxR. Chosen to be relatively (to the other rate constants) high and such that Kdiss (HSL + LuxR) equals 10-6 | |
| kdiss (HSL+LuxR) | 1 s-1 | dissociation rate of the HSL-LuxR complex | |
| kass (HSL+lactonase) | 1E6 s-1 | association rate of HSL with lactonase | |
| kdiss (HSL+lactonase) | 446.5 s-1 | dissociation rate of the HSL-lactonase complex | |
| kcat (HSL:hydroxy-acid) | 29 s-1 | catalytic transformation of HSL to an hydroxy-acid, lactonase is the enzyme | [http://www.jbc.org/cgi/reprint/M311194200v1.pdf link] |
| Dissociation Constants | |||
| KHSL_LuxR | 1E-6 [M]/L | kdiss / kass (HSL+LuxR) | [http://jb.asm.org/cgi/content/full/189/11/4127?view=long&pmid=17400743 link] |
| KHSL_LuxR | 4.05E-6 [M]/L | binding HSL_LuxR on LuxPromotor | [http://parts.mit.edu/igem07/index.php/Tokyo/AHL_assay link] |
| Hill Cooperativity | |||
| nHSL_LuxR | 2.08 | [http://parts.mit.edu/igem07/index.php/Tokyo/AHL_assay link] | |
| Transcription Rates | |||
| kmRNA_LuxR (constitutive promotor) | 0.025 s-1 | see Constitutive Promotors & E. coli transcription Rates | |
| kmRNA_CcdB | 0.025 s-1 | maximal transcription rate for CcdB RNA (no LuxR repressor present) | |
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6T39-3Y6HKD6-BK-1&_cdi=4941&_user=877992&_orig=search&_coverDate=08%2F30%2F1995&_sk=998379998&view=c&wchp=dGLbVtz-zSkzS&md5=49efd14150c71e668eabdef225220ce3&ie=/sdarticle.pdf This paper] says that synthesis of even a few molecules of the shorter CcdB protein is probably lethal.
Models
CellDesigner (SBML file)
Matlab (SBML file)
Remark: not yet up to date to latest (final) version
Simulations
todo!!!
Sensitivity Analysis
todo!!!
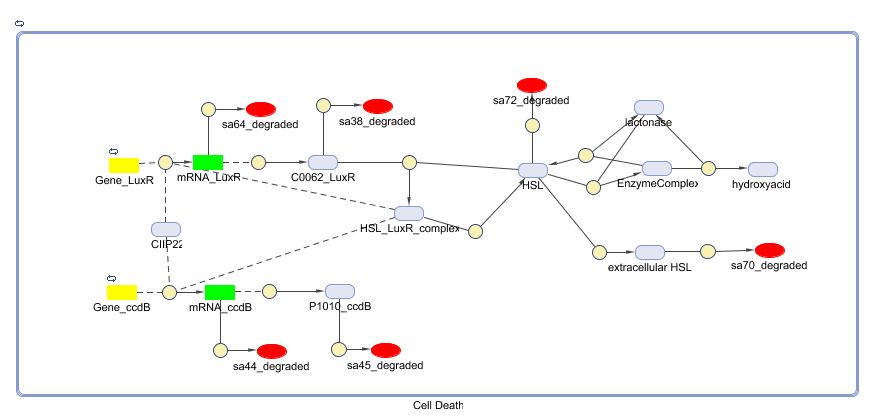
New Cell Death
Extensions to previous system
- During the summer we switched from the above system to a new one which you can see just below, take a look at this figure as it will help you understand the regulation that is present. This new system has a few novelties. First of all, transcription begins at a new hybrid promoter we made: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K145150 BBa_K145150]. This promoter is repressed by c2 P22, which is produced by the memory in the OFF state, making premature activation and cell death impossible. Besides this repression, the promoter is activated by the HSL-LuxR complex originating from a previously activated timer. The promoter behaves as shown schematically below.
- Second, LuxR is now no longer constitutively produced but is placed behind the beforementioned hybrid promoter. This construction mimicks more closely the natural system where LuxR is upregulated when a threshold amount of HSL is present. Plus it also increases the time it takes to activate ccdB, lengthening the timer. The system will now auto-activate if enough HSL is present and the memory is in the ON state.
- Third, the ccdB coding region is also downstream of the hybrid promoter and is thus also subject to the regulation explained above; c2 P22 repression and HSL-LuxR auto-activation. One difference is that the polymerase must first read through a bad terminator with about 60% efficiency before reaching this coding region. Another difference is in the ribosome binding sites preceding both coding regions. Where LuxR can be translated from a RBS with a relative efficiency of 1.00, the ccdB frame can only be read from a 0.01 efficiency RBS.
Describing the system
see also: Project:Cell Death
ODE's
todo!!!
Parameters
| Name | Value | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Degradation Rates | |||
| dLuxR | 9.627044174E-5 s-1 | no LVA tag, so longer lifetime | |
| dcomplex | 9.627044174E-5 s-1 | complex of HSL and LuxR degrades, giving back HSL | |
| dRNA_LuxR | 0.00227 s-1 | [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/picrender.fcgi?artid=124983&blobtype=pdf link] | |
| dccdB | 7.7E-5 s-1 | stable in the absence of ccdA | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8022284?dopt=abstract link] |
| dRNA_ccdB | 0.00231 s-1 | [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/picrender.fcgi?artid=124983&blobtype=pdf link] | |
| dHSL | 1.02E-6 s-1 | very stable in the medium, average lifetime of 185h | [http://aem.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/71/3/1291 link] |
| Association/Dissociation/Reaction Rates | |||
| kass (HSL+LuxR) | 0.002372 s-1 | association rate of HSL with LuxR (estimate from KM but recalculated to remove molar dimension) | |
| kdiss (HSL-LuxR) | 1.0 s-1 | dissociation rate of the HSL-LuxR complex (estimate from KM but recalculated to remove molar dimension) | |
| kass (HSL+lactonase) | 0.002372 s-1 | association rate of HSL with lactonase (estimate from KM but recalculated to remove molar dimension) | |
| kdiss (HSL-lactonase) | 4470.0 s-1 | dissociation rate of the HSL-lactonase complex (estimate from Kd but recalculated to remove molar dimension) | |
| kcat (HSL>>hydroxy-acid) | 29 s-1 | lactonase catalyzed transformation of HSL to a hydroxy-acid | [http://www.jbc.org/cgi/reprint/M311194200v1.pdf link] |
| Dissociation Constants | |||
| KHSL_LuxR | 1E-6 [M] | HSL binding to LuxR | [http://jb.asm.org/cgi/content/full/189/11/4127?view=long&pmid=17400743 link] |
| KHSL_LuxR-promoter | 4.05E-6 [M] | binding of HSL_LuxR complex to the Lux Promotor | [http://parts.mit.edu/igem07/index.php/Tokyo/AHL_assay link] |
| KHSL_lactonase | 4.47E-3 [M] | KM of lactonase with 3OC6HSL | [http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/full/279/14/13645#TBL2 link] |
| Hybrid Promoter | |||
| KC2 P22 | 2.6E-10 [M] | Dissociation constant for P22 c2 promoter binding | [http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/abstract/258/17/10536?maxtoshow=&HITS=10&hits=10&RESULTFORMAT=&andorexactfulltext=and&searchid=1&FIRSTINDEX=0&sortspec=relevance&firstpage=10536&resourcetype=HWCIT link] |
| KHSL_LuxR | 4.05E-6 [M] | Dissociation constant for HSL-LuxR complex promoter binding | [http://jb.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/JB.01443-07v1 link] |
| Hill | 2 | Hill coefficient for P22 c2 binding | [http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/abstract/258/17/10536?maxtoshow=&HITS=10&hits=10&RESULTFORMAT=&andorexactfulltext=and&searchid=1&FIRSTINDEX=0&sortspec=relevance&firstpage=10536&resourcetype=HWCIT link] |
| kleaky | 5E-4 s-1 | transcription rate from the hybrid promoter in the unactivated ON state | |
| kmax | 0.0030 s-1 | maximal transcription rate for the fully activated ON hybrid promoter (might be higher) | |
| Terminator eff | 60.8% | percentage of transcription termination at the B0014 double terminator in front of ccdB | [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0014 link] |
| Translation Rates | |||
| kLuxR translation | 0.556 s-1 | Translation rate for LuxR, B0034 RBS (relative efficiency 1.0) | [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0034 link] |
| kccdB translation | 0.00556 s-1 | Translation rate for ccdB, B0033 RBS (relative efficiency 0.01) | [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0033 link] |
Models
CellDesigner (SBML file)
Matlab (SBML file)
Simulations
todo!!!
Sensitivity Analysis
todo!!!
 "
"