Team:KULeuven/Project/Reset
From 2008.igem.org
m (→Action) |
m |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{:Team:KULeuven/Tools/Styling}} | ||
| + | {{:Team:KULeuven/Tools/Scripting}} | ||
{{:Team:KULeuven/Tools/Header}} | {{:Team:KULeuven/Tools/Header}} | ||
| - | + | [[Image:logo_reset.jpg|120px|right]] | |
==Reset== | ==Reset== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
===Components=== | ===Components=== | ||
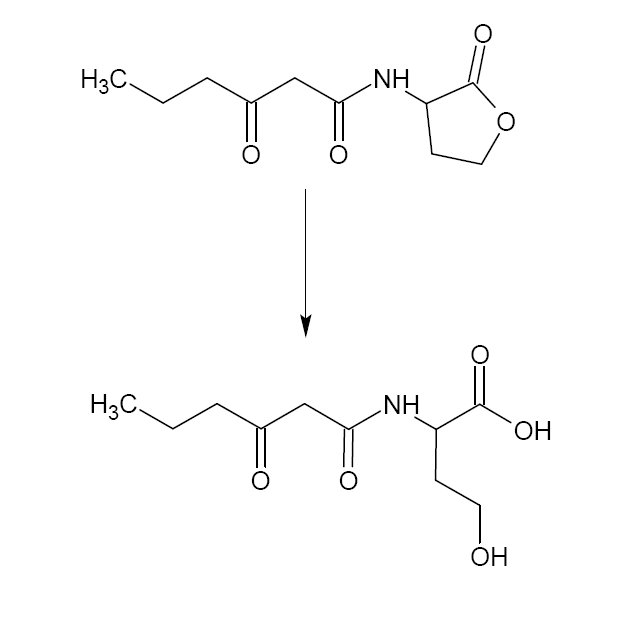
| - | The system is dependent on the output of the filter, and has | + | The system is dependent on the output of the filter, and has therefore got a T7 RNA polymerase promoter ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I712074 '''BBa_I712074''']) followed by a RiboLock ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J23078 '''BBa_J23078''']). The ''aiiA'' gene ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_C0060 '''BBa_C0060''']), short for autoinducer inactivation, is placed downstream of this AND-gate and codes for lactonase, an enzyme that hydrolyses the 3OC6HSL ester bonds. ([http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v411/n6839/full/411813a0.html reference]) |
===Action=== | ===Action=== | ||
| - | + | This device was conceived to reset the [https://2008.igem.org/Team:KULeuven/Project/Inverter Timer]. | |
| - | + | When significant input (re-)emerges, lactonase is produced. It will then convert all available intracellular 3OC6HSL at that time to a hydroxy-acid, thereby inactivating and efficiently removing it from the active system. This way, the timer is reset and the cell may live to see another day. | |
| + | |||
| + | Originally, a device generating a pulse of lactonase was thought to do the job, but modeling suggested that the amount of lactonase produced during this pulse was too small to accomplish a thorough reset of our system. So the device was reinvented and a simplified (non-pulse) version was devised and described here. Now the amount of lactonase produced should be high enough for the reset to function properly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{:Team:KULeuven/Tools/Components}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:51, 3 October 2008
Contents |
Reset
BioBricks
Components
The system is dependent on the output of the filter, and has therefore got a T7 RNA polymerase promoter ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I712074 BBa_I712074]) followed by a RiboLock ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J23078 BBa_J23078]). The aiiA gene ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_C0060 BBa_C0060]), short for autoinducer inactivation, is placed downstream of this AND-gate and codes for lactonase, an enzyme that hydrolyses the 3OC6HSL ester bonds. ([http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v411/n6839/full/411813a0.html reference])
Action
This device was conceived to reset the Timer.
When significant input (re-)emerges, lactonase is produced. It will then convert all available intracellular 3OC6HSL at that time to a hydroxy-acid, thereby inactivating and efficiently removing it from the active system. This way, the timer is reset and the cell may live to see another day.
Originally, a device generating a pulse of lactonase was thought to do the job, but modeling suggested that the amount of lactonase produced during this pulse was too small to accomplish a thorough reset of our system. So the device was reinvented and a simplified (non-pulse) version was devised and described here. Now the amount of lactonase produced should be high enough for the reset to function properly.
 "
"



 Input
Input Output
Output Filter
Filter InverTimer
InverTimer Reset
Reset Cell Death
Cell Death Memory
Memory