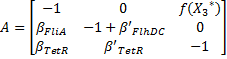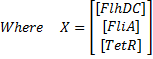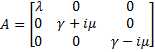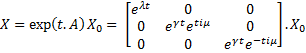Team:Paris/Modeling/BOB/Simulations page travail
From 2008.igem.org
(→Understanding the dynamics) |
(→Using these elements to improve the system and give directions to the wet-lab) |
||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
=== Using these elements to improve the system and give directions to the wet-lab === | === Using these elements to improve the system and give directions to the wet-lab === | ||
| - | + | * What can we do about that, ans how can we improve the behavior of the system? The ideal though process would be to get the equilibrium state, but not with numerical values, so as to understand the influence of each of the system parameter. However, we face a major problem. This requires ot solve an (n+1) degree equation, which explicit solutions are unusable. Yet, imagining that we can get the solution, we could evaluate the eigenvalues in the same way (since they are solution of a third degree equation, this could be possible). Consequently, we could understand the influence of each parameter, and we could find a way to minimize the λ and γ coefficients. | |
| - | + | * However, we understand that even though we consider the short system, this process faces strong difficulties. Yet, it is possible to consider an algorithmic approach that meets the same ends. Let's say we want to otpimize the system for n and θ<sub>FlhDC</sub> : | |
| - | + | ** for n evolving between n<sub>min</sub> and n<sub>max</sub> | |
| + | ** for θ<sub>FlhDC</sub><sub>min</sub> | ||
== Entire System == | == Entire System == | ||
Revision as of 10:47, 7 October 2008
|
(Under Construction : synchronisation and whole system)
Simulations and Mathematical analysis
OscillationsShort System
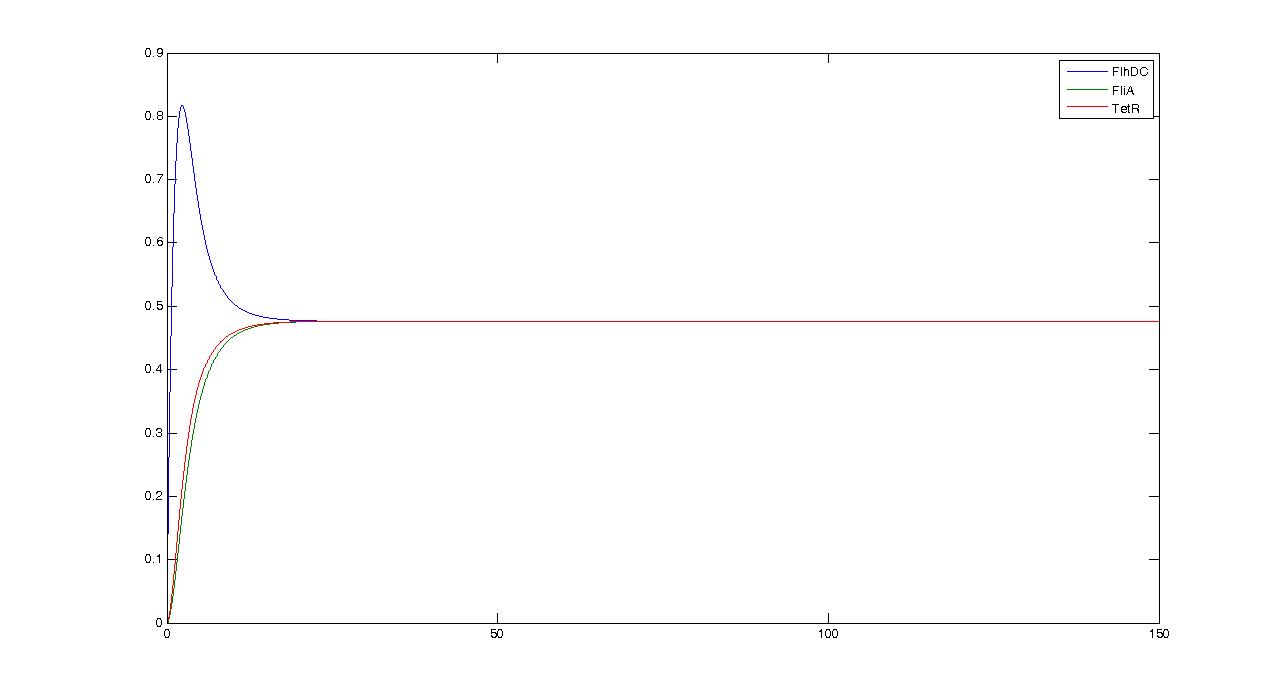
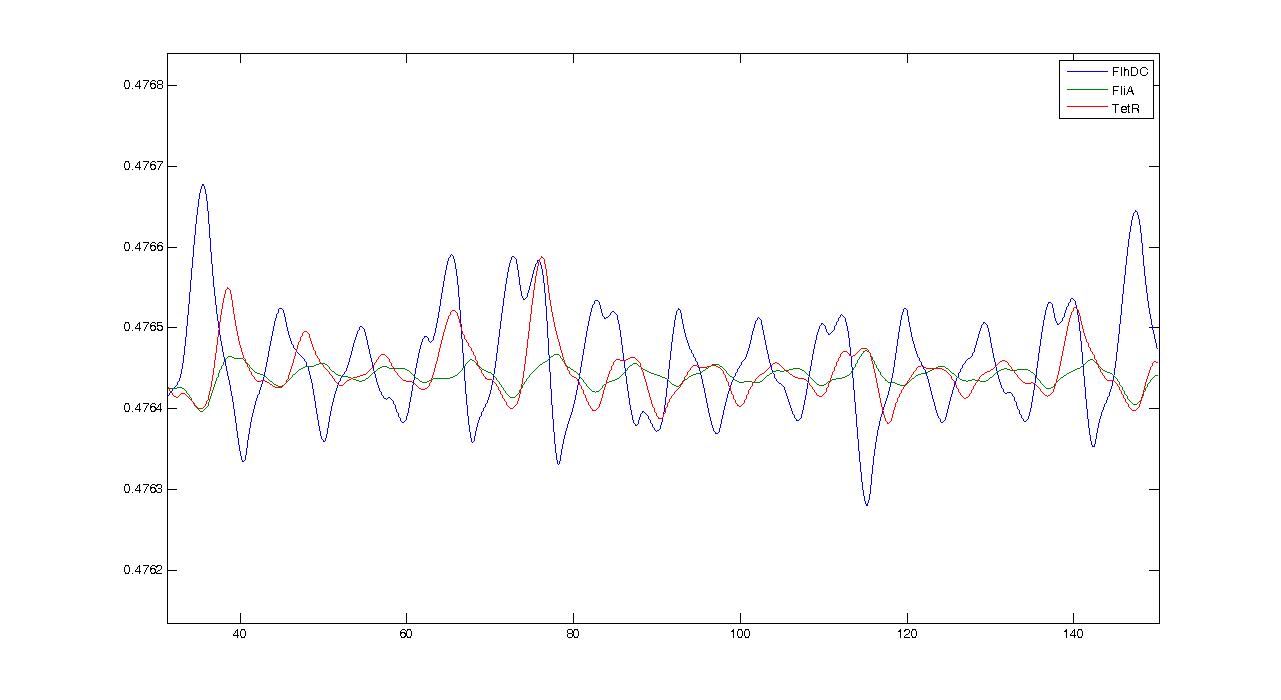
Observations---> petites oscillations + vérifier par le calcul ---> trop grande réactivité de flhDC
Understanding the dynamics
Then, we evaluate the jacobian matrix, so as to put the system under its linearized form:
which gives : Then, we want to find the eigenvalues of the jacobian matrix, because they make us understand the behavior of the system. Here is the theoretical explanation : The λ and γ coefficients make the convergence. In our case they are negative terms, which explains the fact that we have a quick convergence for the system. Ideally, it could be convenient to find which parameter influence this coefficient, so as to play with it and be able to propose a better control of the convergence.
We obtained three solutions : -0.2382 - 0.6139i -0.2382 + 0.6139i 0.4764 We are only interested in positive real solutions. We can note that 0.4764 corresponds well to the experimental equilibrium value. Then we evaluated the eigenvalues for the jacobian : -1.0159 + 0.5042i -1.0159 - 0.5042i -0.1111 We can note that the λ and γ coefficient are negative, which corroborates the fact that we obtain a convergence. Finally for since μ=0.5042 we find a theoretical period of Ttheoretical=12.4617. Experimentally, we find Texperimental~10. We can see that some numerical noise must be involved, which gives the reading of the period quite tough. However, we get the same order of magnitude, which proves that the oscillations are occuring, though quietly!Using these elements to improve the system and give directions to the wet-lab
Entire System//biocham ici//+ comparaison avec le modele hillistique FIFO
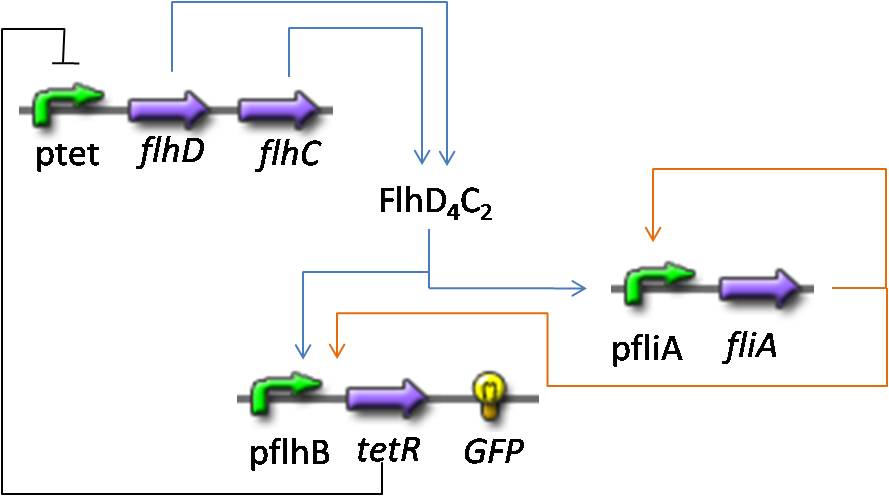
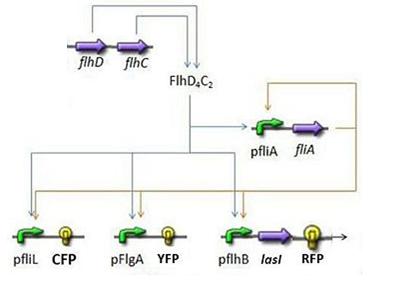
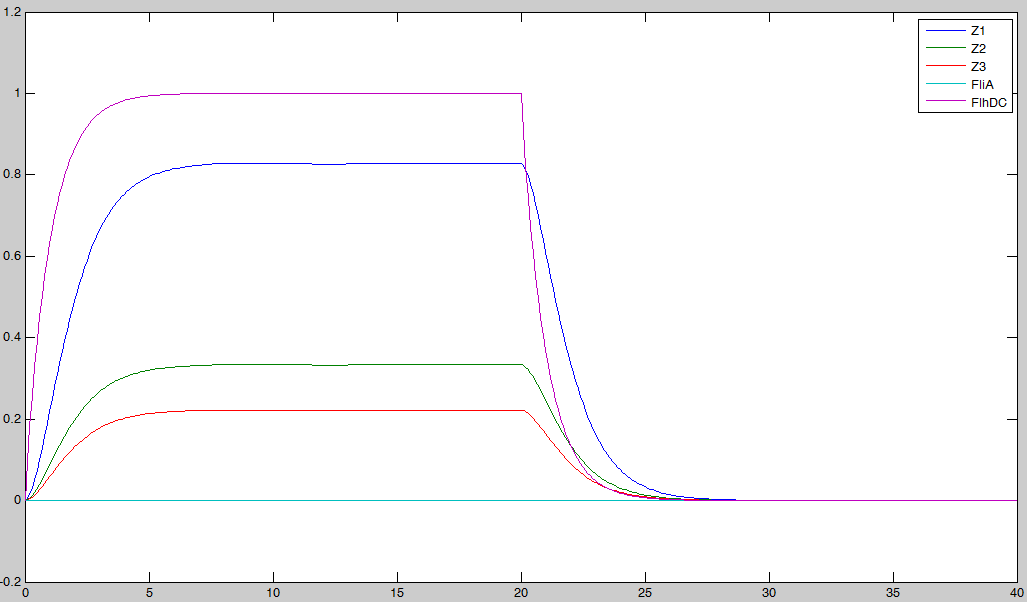
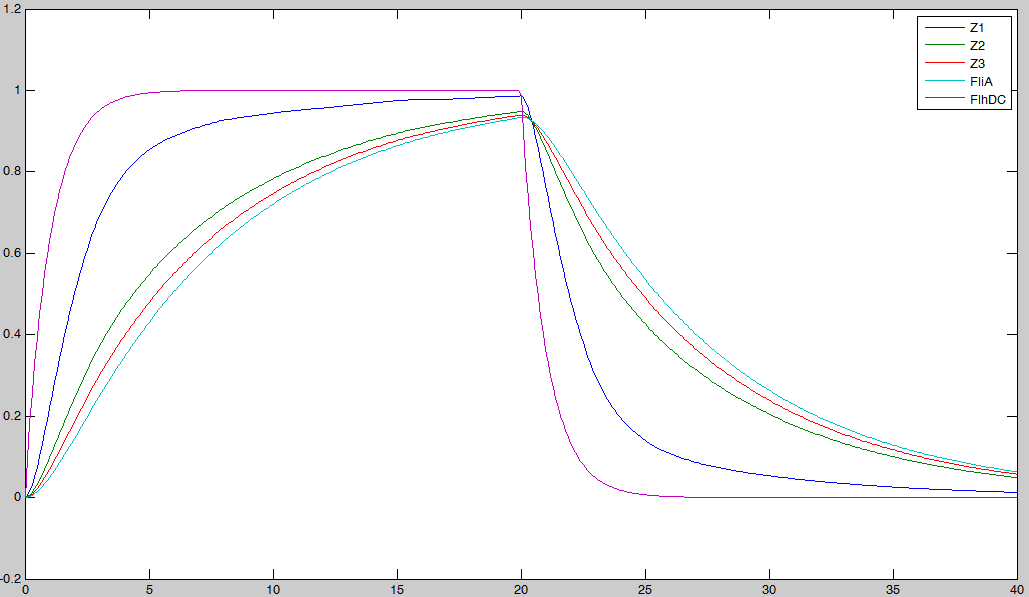
Here is the system we implementated using Matlab (see the corresponding codes) and the corresponding equations (for more detailed information see our establishment of the model). where CFP, YFP, and RFP will be denoted below as respectively Z1,Z2 and Z3.
In fact we assumed that this behavior for FlhDC was acceptable regarding its estimated behavior in the whole system.
We may see that there is a LIFO behavior rather than the FIFO we expect...
SynchronizationMathematical AnalysisSimulations and verification of the hypothesis |
|||||||||||||||||||
 "
"