Team:Freiburg Cloning Strategy
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 934: | Line 934: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| - | <br><br><br> | + | <br><br><br><br> |
'''METHODS''' <br> | '''METHODS''' <br> | ||
| - | _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ | + | _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________<br><br> |
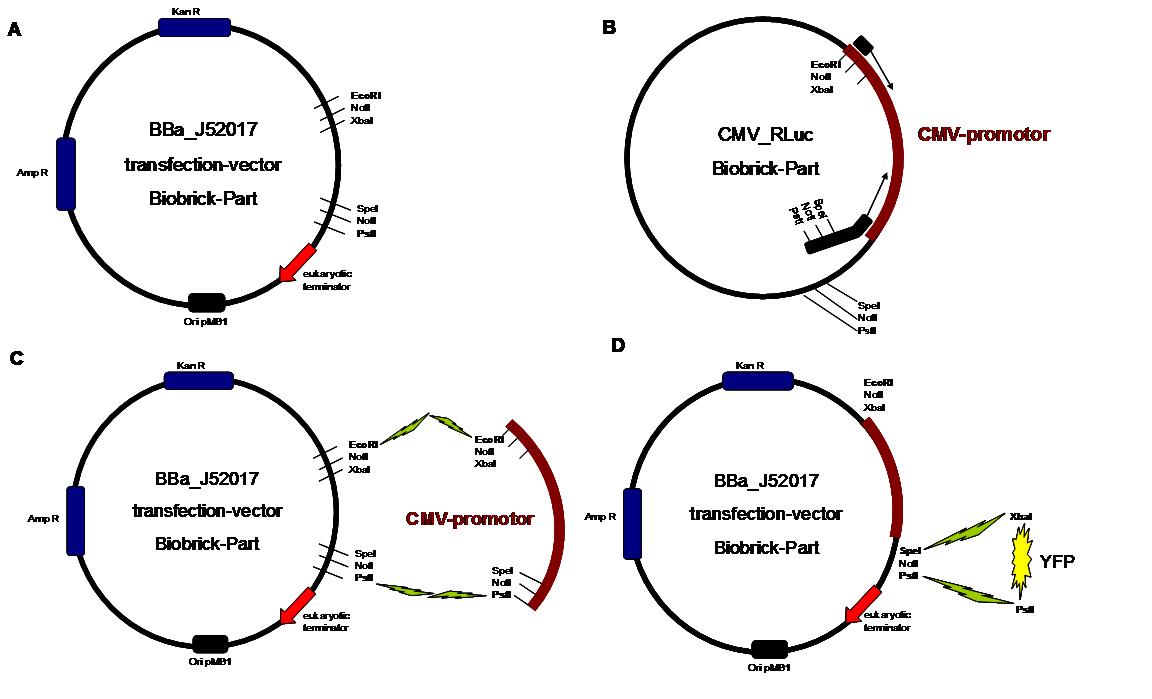
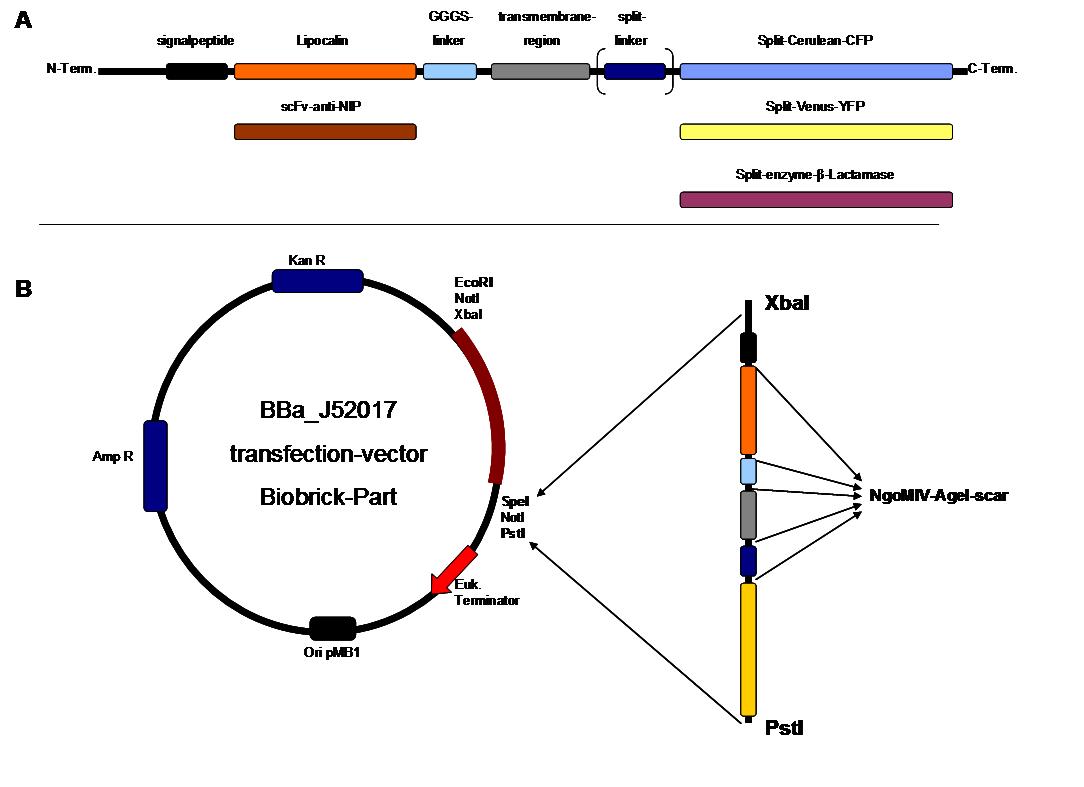
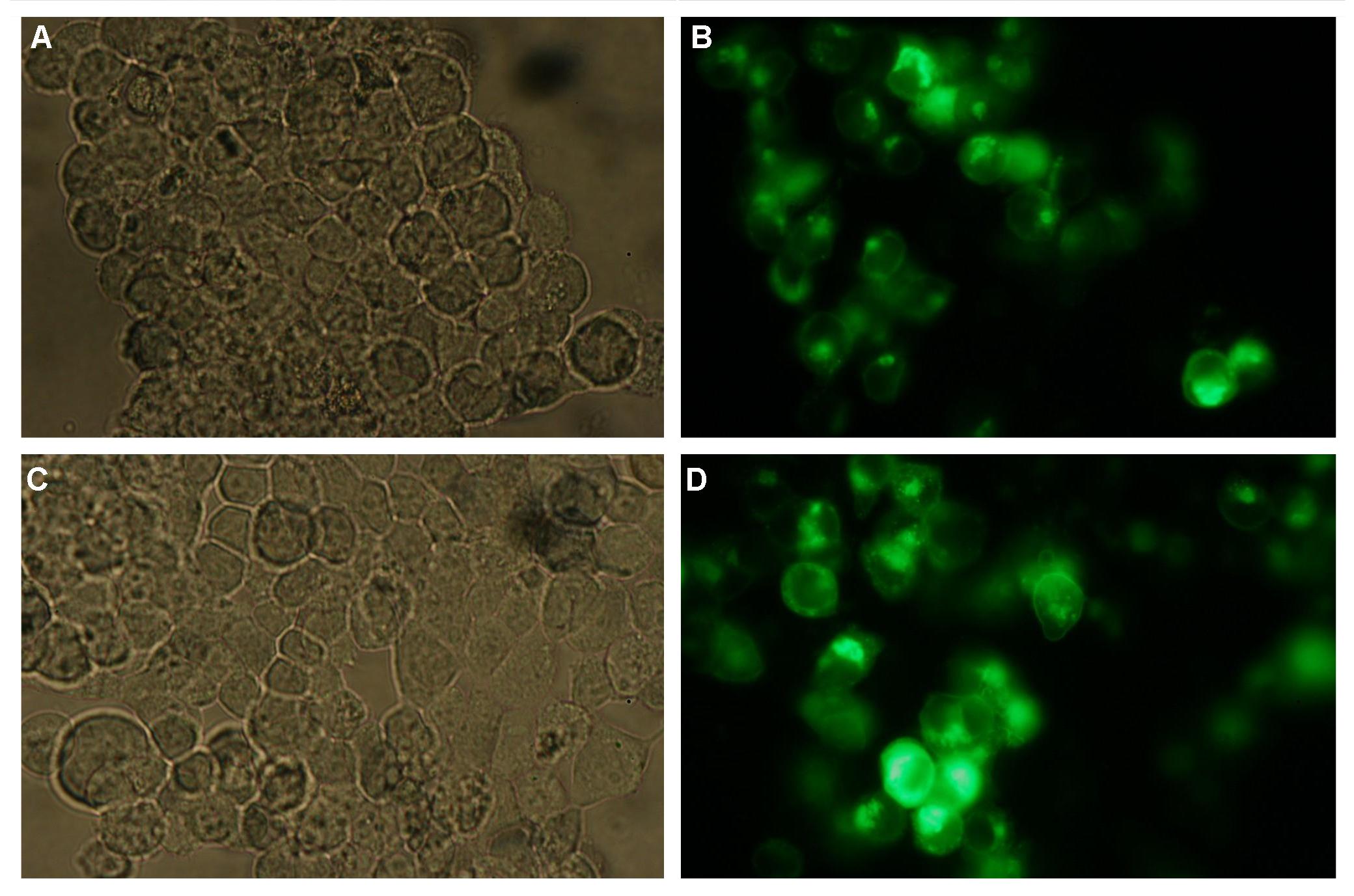
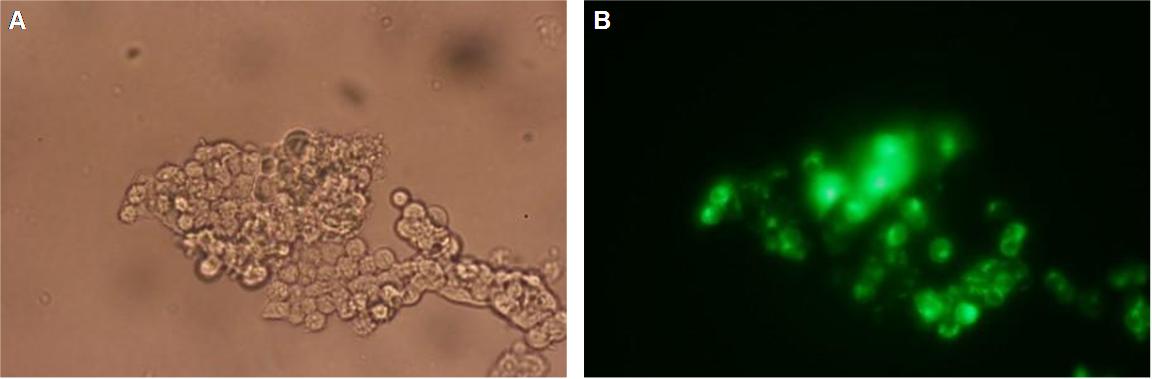
The cloning was started with a preparative digestion of the DNA-Plasmids. To clone fusion parts the vector constructs were digested with AgeI and PstI to open the Biobrick suffix. The inserts were digested with NgoMIV and PstI. For cloning into the transfection-vector the enzymes SpeI and PstI were used for vector and XbaI, PstI for insert to keep up the ATG-start codon in the XbaI restriction site of the biobrick suffix. All restriction-enzymes were ordered from New England Biolabs. After digestion the DNA-fragments were separated on a 1% agarose gel. The DNA-band of interest was isolated and purified with the QIAGEN QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit. For the ligation a 3 molar excess of the insert was put together with the vector-fragment and ligated with a Quick ligase (New England Biolabs). After half an our at room temperature the DNA was transformed to chemical competent E.coli strain XL1 cells, plated on 2YT-agar-plates and incubated at 37°C over night. After picking clones and growing in 5ml LB-medium, the plasmid DNA was isolated by QIAGEN QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit. A test digestion was prepared with about 0,5µg Plasmid DNA and NotI restriction enzyme to isolate the fusion-protein from the vector and to control if the expected bands were obtained. After a positive result the clones were sent to GATC-Biotech for sequencing. | The cloning was started with a preparative digestion of the DNA-Plasmids. To clone fusion parts the vector constructs were digested with AgeI and PstI to open the Biobrick suffix. The inserts were digested with NgoMIV and PstI. For cloning into the transfection-vector the enzymes SpeI and PstI were used for vector and XbaI, PstI for insert to keep up the ATG-start codon in the XbaI restriction site of the biobrick suffix. All restriction-enzymes were ordered from New England Biolabs. After digestion the DNA-fragments were separated on a 1% agarose gel. The DNA-band of interest was isolated and purified with the QIAGEN QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit. For the ligation a 3 molar excess of the insert was put together with the vector-fragment and ligated with a Quick ligase (New England Biolabs). After half an our at room temperature the DNA was transformed to chemical competent E.coli strain XL1 cells, plated on 2YT-agar-plates and incubated at 37°C over night. After picking clones and growing in 5ml LB-medium, the plasmid DNA was isolated by QIAGEN QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit. A test digestion was prepared with about 0,5µg Plasmid DNA and NotI restriction enzyme to isolate the fusion-protein from the vector and to control if the expected bands were obtained. After a positive result the clones were sent to GATC-Biotech for sequencing. | ||
The GGGS-Linker was produced by Klenow -fill-in-PCR. Two primers were designed align to each other at 60°C and filled to a complete dobble-strand by Klenow Polymerase fragment.<br> | The GGGS-Linker was produced by Klenow -fill-in-PCR. Two primers were designed align to each other at 60°C and filled to a complete dobble-strand by Klenow Polymerase fragment.<br> | ||
Revision as of 10:15, 28 October 2008
 "
"