Team:UC Berkeley/LayeredAssembly
From 2008.igem.org
Contents |
Project Motivation
Imagine a world with no mini-preps. A world where DNA extraction and purification could be accomplished in a single eppendorf tube. We did, and so we created CloneBots, an automated approach to synthetic biology. CloneBots seeks to simplify and automate the cloning process by creating protocols that involves only liquid handling steps that could more readily be performed by robots. We have accomplished this by genetically encoding many of the required steps into the E. coli, thereby allowing the cells to perform the required protocols in-vivo.
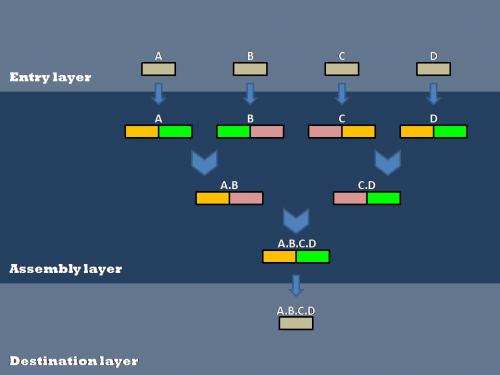
Our efforts to optimize synthetic biology protocols centered around the layered assembly scheme used by the Anderson Lab at UC Berkeley. Layered assembly is a straight-forward and robust method for combining two or more basic parts into a destination vector[[Image:data. There are three layers (Entry, Assembly and Destination). Both Entry and Assembly layers are standardized for ease of use, while the Destination plasmid can be tailored to a specific experiment or assay.
Layered Assembly
Biobrick parts are created in an entry vector and then transferred to double antibiotic assembly vectors (antibiotic resistances shown in orange, green, and pink), followed by subsequent assembly steps to connect various parts(A, B, C, and D). After all of the assembly steps are complete, the desired composite parts can then be transferred into the destination vector of choice.
Entry Layer
The Entry plasmid contains a Spectinomycin antibiotic resistance marker and EcoRI, BglII and BamHI restriction sites. All basic parts are cloned into the entry vector. The basic part is flanked by attR1 and attr2 recombination sites. File:Entry plasmdi
Since the entry plasmid attR1 and attR2 recombination sites, the basic part can easily be transferred into one of six different assembly vectors using the Gateway cloning scheme described here [[1]].
Assembly Layer
The assembly layer is used to combine two or more basic parts in a specified order to create the desired composite part. The assembly plasmid contains two antibiotic resistance genes, carefully chosen to simplify screening for the correct composite part separated by a XhoI restriction site. The basic parts are flanked by BglII and BamHI restriction sites. For details on the two-antibiotic assembly scheme, click here
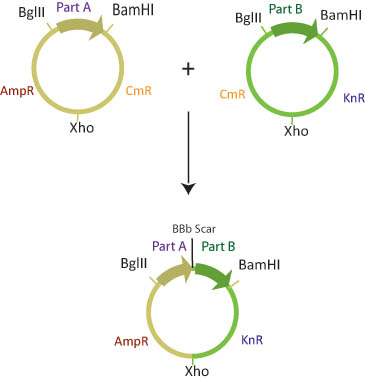
Destination Layer
Completed composite parts are transferred from the assembly layer to the destination layer using the Gateway cloning scheme [[2]]. The Destination plasmid is tailored to a specific experiment or assay. This allows a single composite part to be transfered to several different Destination plasmids for further experimentation or characterization.
Issues with Current Methods
1) Gateway reactions, used for transferring basic parts into the assembly plasmids and transferring composite parts into destination plasmids, are expensive ($6-$7/reaction).
2) Current protocol with no gel purification step is inefficent a. Currently protocol involves gel purification and is required to select the correct basic part after assembly.
 "
"