Team:KULeuven/Project/CellDeath
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Components) |
(→Action) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
===Action=== | ===Action=== | ||
When the concentration of HSL is big enough (see the [https://2008.igem.org/Team:KULeuven/Model/CellDeath#CellDesigner_.28SBML_file.29 modeling page]), HSL will form a complex with the LuxR protein and thus activate the LuxpR promoter. This results in ''ccdB'' production and eventually in cell death ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10196173?dopt=Abstract reference]). | When the concentration of HSL is big enough (see the [https://2008.igem.org/Team:KULeuven/Model/CellDeath#CellDesigner_.28SBML_file.29 modeling page]), HSL will form a complex with the LuxR protein and thus activate the LuxpR promoter. This results in ''ccdB'' production and eventually in cell death ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10196173?dopt=Abstract reference]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Extensions to previous system=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * During the summer we switched from the above system to a new one which you can see just below, take a look at this figure as it will help you understand the regulation that is present. This new system has a few novelties. First of all, transcription begins at a new hybrid promoter we made: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K145150 '''BBa_K145150''']. This promoter is repressed by c2 P22, which is produced by the memory in the OFF state, making premature activation and cell death impossible. Besides this repression, the promoter is activated by the HSL-LuxR complex originating from a previously activated timer. The promoter behaves as shown schematically below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Hybrid_promotor.PNG|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Second, LuxR is now no longer constitutively produced but is placed behind the beforementioned hybrid promoter. This construction mimicks more closely the natural system where LuxR is upregulated when a threshold amount of HSL is present. Plus it also increases the time it takes to activate ccdB, lengthening the timer. The system will now auto-activate if enough HSL is present and the memory is in the ON state. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Third, the ccdB coding region is also downstream of the hybrid promoter and is thus also subject to the regulation explained above; c2 P22 repression and HSL-LuxR auto-activation. One difference is that the polymerase must first read through a bad terminator with about 60% efficiency before reaching this coding region. Another difference is in the ribosome binding sites preceding both coding regions. Where LuxR can be translated from a RBS with a relative efficiency of 1.00, the ccdB frame can only be read from a 0.01 efficiency RBS. | ||
| + | |||
{{:Team:KULeuven/Tools/Components}} | {{:Team:KULeuven/Tools/Components}} | ||
Revision as of 12:30, 2 September 2008
dock/undock dropdown
Contents |
Cell Death
BioBricks
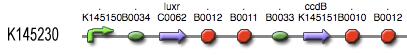
Components
The luxR protein BBa_C0062 is placed under control of a P22 CII hybrid promoter BBa_145150. The ccdB suicide gene BBa_P1010, on its part, is placed under control of the LuxpR promoter BBa_R0062.
Action
When the concentration of HSL is big enough (see the modeling page), HSL will form a complex with the LuxR protein and thus activate the LuxpR promoter. This results in ccdB production and eventually in cell death (reference).
Extensions to previous system
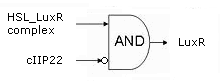
- During the summer we switched from the above system to a new one which you can see just below, take a look at this figure as it will help you understand the regulation that is present. This new system has a few novelties. First of all, transcription begins at a new hybrid promoter we made: BBa_K145150. This promoter is repressed by c2 P22, which is produced by the memory in the OFF state, making premature activation and cell death impossible. Besides this repression, the promoter is activated by the HSL-LuxR complex originating from a previously activated timer. The promoter behaves as shown schematically below.
- Second, LuxR is now no longer constitutively produced but is placed behind the beforementioned hybrid promoter. This construction mimicks more closely the natural system where LuxR is upregulated when a threshold amount of HSL is present. Plus it also increases the time it takes to activate ccdB, lengthening the timer. The system will now auto-activate if enough HSL is present and the memory is in the ON state.
- Third, the ccdB coding region is also downstream of the hybrid promoter and is thus also subject to the regulation explained above; c2 P22 repression and HSL-LuxR auto-activation. One difference is that the polymerase must first read through a bad terminator with about 60% efficiency before reaching this coding region. Another difference is in the ribosome binding sites preceding both coding regions. Where LuxR can be translated from a RBS with a relative efficiency of 1.00, the ccdB frame can only be read from a 0.01 efficiency RBS.
 "
"


 Input
Input Output
Output Filter
Filter InverTimer
InverTimer Reset
Reset Cell Death
Cell Death Memory
Memory