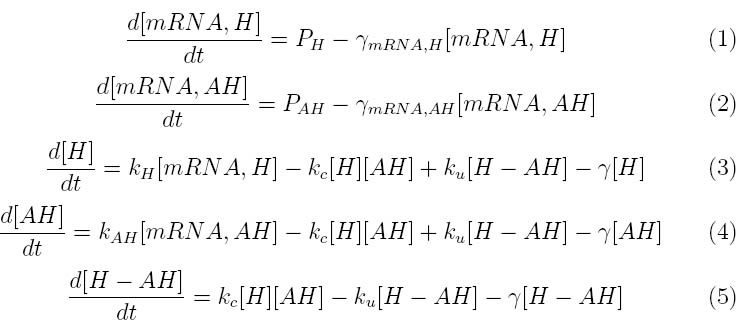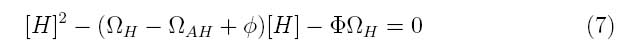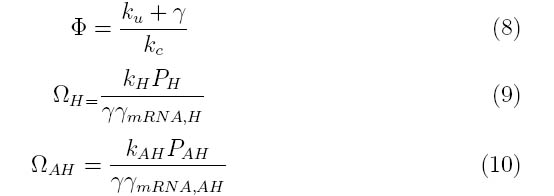Team:UC Berkeley/Modeling
From 2008.igem.org
The kinetics of the Lambda phage lysis device was modeled to help our team gain an insight into the behavior of our system. The below equations describe our system
Where P_H and P_AH represent the mRNA promoter strengths, gamma_mRNA,H and gamma_mRNA,AH are the degradation rates for holin and antiholin respectively and gamma is the protein degradation rate, k_H , k_AH and k_c represent the rate constants for holin and antiholin formation and the coupling rate for the holin-antiholin dimer.
At steady state,
The system can be simplified into the following transfer function
Where the system can be divided into three dimensionless parameters which describe the behavior of holin, antiholin and the holin-antiholin dimer
Using MatLab, the following graph of the system was produced.
The literature indicates that at the time of lysis, cells infected with lambda phage have approximately 1000 holin proteins. Therefore, the critical concentration of holin (Hc) was set at 1000 holin proteins per cell.
The horizontal line at y=1 represents the critical holin concentration needed induce lysis.
 "
"