Team:TUDelft/Temperature design2
From 2008.igem.org
Bavandenberg (Talk | contribs) (→Design approach) |
Bavandenberg (Talk | contribs) (→Design approach) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
<gallery Caption="Design starting point"> | <gallery Caption="Design starting point"> | ||
Image:Tudelft_design_starting_point.png | Full RNA thermometer | Image:Tudelft_design_starting_point.png | Full RNA thermometer | ||
| - | Image:Tudelft_design_starting_point_hairpin.png | | + | Image:Tudelft_design_starting_point_hairpin.png | Temperature sensitive hairpin |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 08:59, 2 September 2008
>> Work in progress
Contents |
Parts Design II
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K115016 BBa:K115016], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K115017 BBa:K115017], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K115018 BBa:K115018], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K115019 BBa:K115019]
Changing the temperature threshold
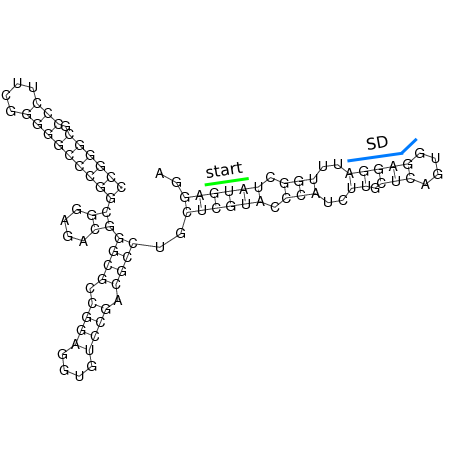
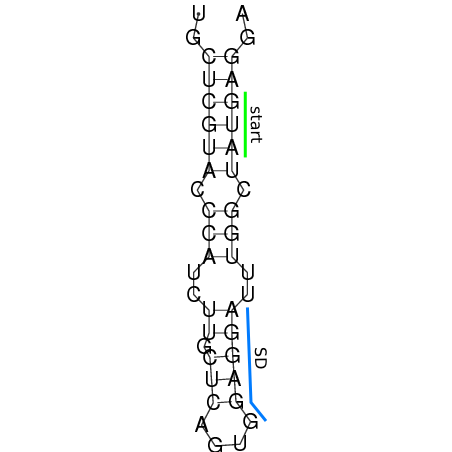
The principle of the RNA thermometer is based on base pairing between the nucleotides in the Shine Dalgarno region. At a certain temperature the RNA is folded into a structure in which base pairing nucleotides make the Shine Dalgarno region unreachable for the ribosome. With a rise in temperature, the binding forces between the base pairing nucleotides decrease and above a certain threshold temperature the base pairing forces are to weak to hold the base pairing nucleotides together, causing the RNA to (partially) unfold. The binding between the base pairing nucleotides let loose causing the RNA to unfold, exposing the Shine-Dalgarno region and thereby enabling the ribosome to initiate translation.
When only looking at this principle, an RNA thermometer with a different temperature threshold can be designed by simply increasing or decreasing the binding forces of the base-pairing nucleotides in the Shine-Dalgarno region, shifting the temperature threshold to a higher or lower temperature respectively (fig). Increasing the binding forces could be achieved by incorporating base pairing C and G nucleotides, which bind relatively strong forming a stable helix. Decreasing the binding forces could be done by introducing less strong binding nucleotide base-pairs, such as A-U and G-U base pairs, forming a less stable helix.
But things are not that easy. At first, adding mutations in order to enforce or weaken the temperature sensitive region can also cause the RNA to fold into a completely different structure. This way it can loose its function as an RNA thermometer. Secondly, there are some constraints to the possible mutations; the start codon and the Shine Dalgarno sequence must off course remain unaltered and in case of a standard biobrick the scar must also be part of the temperature sensitive region (see the scar problem). Third, although it seems that only a thermosensitive hairpin is needed to have a functioning RNA thermometer (as described in the analysis section) there could very well be more factors that are of influence on the functioning and temperature threshold of the RNA thermometer that are still unknown.
Design approach
In order to design an RNA thermometer with a different temperature threshold an existing RNA thermometer is taken as a starting point. The one chosen is a ROSE RNA thermometer from Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/viewer.fcgi?db=nucleotide&val=NC_004463 NC_004463]) residing at location [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/sviewer/?id=NC_004463.1&v=5784144-5784239 5784144-5784239] which is at the 5' side of the gene [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1051455&ordinalpos=2&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Gene.Gene_ResultsPanel.Gene_RVDocSum hspB].
Design requirements
References
- ^ De Smit M H, Van Duijn J (1990). "Secondary structure of the ribosome binding site determines translation efficiency: A quantitative analysis". PNAS, 1990-10, vol.87, no.19, 7668-7672. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2217199 PMID:2217199]
- ^ Hoe N P, Goguen J D (1993). "Temperature sensing in Yersinia pestis: Translation of the LcrF activator protein is thermally regulated". J Bacteriol, 1993 December, 175(24), 7901-7909. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7504666 PMID:7504666]
- ^ Chowdhurry S, Maris C, Allain F H T, Narberhaus F (2006). "Molecular basis for temperature sensing by an RNA thermometer". The EMBO Journal, 2006, 25, 2487–2497. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16710302 PMID:16710302]
- ^ Nocker A, Hausherr T, Balsiger S, Krstulovic N, Hennecke H, Narberhaus F (2001). "A mRNA-based thermosensor controls expression of rhizobial heat shock genes". Nucleic Acids Research, 2001 December 1, 29(23):4800-4807. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11726689 PMID:11726689]
- ^ Balsiger S, Ragaz C, Baron C, Narberhaus F. "Replicon-specific regulation of small heat shock genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens". Journal of Bacteriology, October 2004, p. 6824-6829, Vol.186, No.20. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15466035 PMID:15466035]
- ^ Waldminghaus T, Heidrich N, Branti S, Narberhaus F (2007). "FourU: a novel type of RNA thermometer in Salmonella". Molecular Microbiology, Volume 65, Issue 2, 413-424. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17630972 PMID:17630972]
- ^ Johansson J, Mandin P, Renzoni A, Chiaruttinni C, Springer M, Cossart P. "An RNA thermosensor controls expression of virulance genes in Listeria monocytogenes". Cell , Volume 110 , Issue 5 , 551-561. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12230973 PMID:12230973]
 "
"