Team:TUDelft/Color modeling
From 2008.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
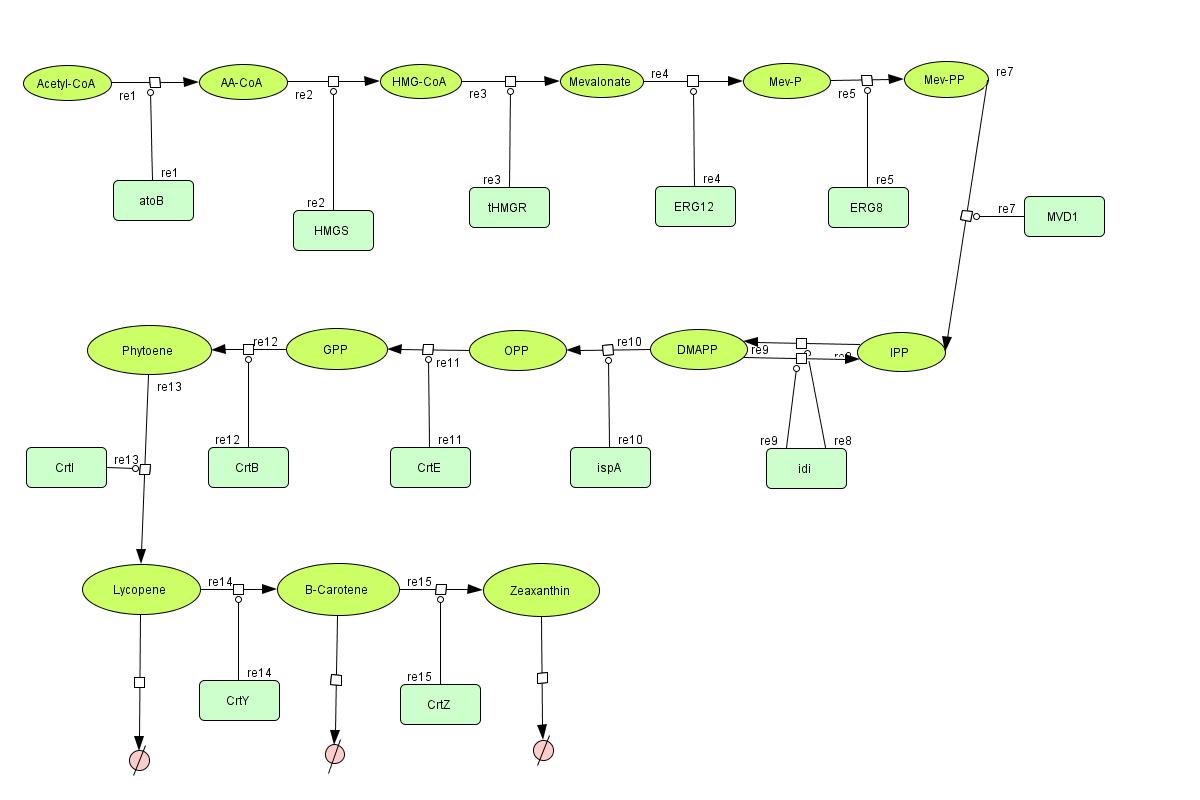
In the output we use [http://www.lbl.gov/Science-Articles/Archive/assets/images/2004/Mar-24/Engineering_terpenoids.pdf mevalonate] and [http://parts.mit.edu/igem07/index.php/Image:Zeaxanthin.jpg GPP] pathways together to produce red, orange and yellow colors. | In the output we use [http://www.lbl.gov/Science-Articles/Archive/assets/images/2004/Mar-24/Engineering_terpenoids.pdf mevalonate] and [http://parts.mit.edu/igem07/index.php/Image:Zeaxanthin.jpg GPP] pathways together to produce red, orange and yellow colors. | ||
The biosynthetic model is bulit in '''CellDesigner™'''. There are 14 subtrates and 13 enzymes in total. The last three subtrates are the color products and are consuming so we have degradation links for them. Lycopene, B-carotene and Zeaxanthin give red, orange and yellow colors respectively. | The biosynthetic model is bulit in '''CellDesigner™'''. There are 14 subtrates and 13 enzymes in total. The last three subtrates are the color products and are consuming so we have degradation links for them. Lycopene, B-carotene and Zeaxanthin give red, orange and yellow colors respectively. | ||
| + | For the 14 reactions of enzyme-subtrate the Michaelis-Menten kinetics is applied and we have the mass action kinetics for the three degradations. | ||
[[Image:Mevalonate.jpg |600px]] | [[Image:Mevalonate.jpg |600px]] | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 21 August 2008
In the output we use mevalonate and GPP pathways together to produce red, orange and yellow colors. The biosynthetic model is bulit in CellDesigner™. There are 14 subtrates and 13 enzymes in total. The last three subtrates are the color products and are consuming so we have degradation links for them. Lycopene, B-carotene and Zeaxanthin give red, orange and yellow colors respectively. For the 14 reactions of enzyme-subtrate the Michaelis-Menten kinetics is applied and we have the mass action kinetics for the three degradations.
 "
"